Effects of arginine in therapeutic protein formulations: a decade review and perspectives
- PMID: 38075239
- PMCID: PMC10702853
- DOI: 10.1093/abt/tbad022
Effects of arginine in therapeutic protein formulations: a decade review and perspectives
Abstract
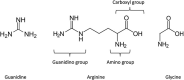
Arginine (Arg) is a natural amino acid with an acceptable safety profile and a unique chemical structure. Arg and its salts are highly effective in enhancing protein refolding and solubilization, suppressing protein-protein interaction and aggregation and reducing viscosity of high concentration protein formulations. Arg and its salts have been used in research and 20 approved protein injectables. This review summarizes the effects of Arg as an excipient in therapeutic protein formulations with the focus on its physicochemical properties, safety, applications in approved protein products, beneficial and detrimental effects in liquid and lyophilized protein formulations when combined with different counterions and mechanism on protein stabilization and destabilization. The decade literature review indicates that the benefits of Arg overweigh its risks when it is used appropriately. It is recommended to add Arg along with glutamate as a counterion to high concentration protein formulations on top of sugars or polyols to counterbalance the negative effects of Arg hydrochloride. The use of Arg as a viscosity reducer and protein stabilizer in high concentration formulations will be the inevitable future trend of the biopharmaceutical industry for subcutaneous administration.
Keywords: antibody; arginine; excipient; high concentration formulation; protein stabilization; subcutaneous injection; therapeutic proteins; viscosity reduction.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Antibody Therapeutics. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Steven Ren is an employee and shareholder of WuXi Biologics. The author reports no other potential conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
References
-
- Rudolph, R., Fischer, S. (1990) US patent, 4,434.
-
- Lange, C, Rudolph, R. Suppression of protein aggregation by L-arginine. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2009; 10: 408–14. - PubMed
-
- Arakawa, T, Tsumoto, K, Kita, Yet al. Biotechnology applications of amino acids in protein purification and formulations. Amino Acids 2007; 33: 587–605. - PubMed
-
- Ishibashi, M, Tsumoto, K, Tokunaga, Met al. Is arginine a protein-denaturant? Protein Expr Purif 2005; 42: 1–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources