Simple analytical method using ultraviolet spectral dataset and chemometrics for the authentication of Indonesian specialty ground roasted coffee with different botanical and geographical indications
- PMID: 38075611
- PMCID: PMC10701359
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2023.109820
Simple analytical method using ultraviolet spectral dataset and chemometrics for the authentication of Indonesian specialty ground roasted coffee with different botanical and geographical indications
Abstract
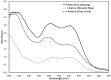
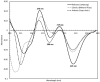
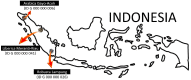
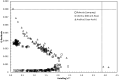
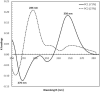
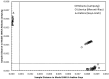
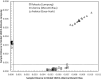
The possible application of a simple analytical method based on a UV (ultraviolet) spectral dataset coupled with SIMCA (soft independent modeling of class analogy) for authentication of Indonesian specialty ground roasted coffee with different botanical and geographical indications (GIs) was demonstrated. Three types of Indonesian specialty ground roasted coffee were used: GIs arabica coffee from Gayo Aceh (96 samples), GIs liberica coffee from Meranti-Riau (119 samples), and GIs robusta coffee from Lampung (150 samples) with 1 g weight of each sample. All samples were extracted using hot distilled water and 3 mL aqueous filtered samples were pipetted into a 10 mm quartz cell. Original UV spectral datasets were recorded in the range of 190-399 nm. The pre-processed spectral dataset was generated using three simultaneous different preprocessing techniques: moving average smoothing with 11 segments, standard normal variate (SNV), and Savitzky-Golay (SG) first derivative with window size and polynomial order value of 11 and 2. The supervised classification based on the SIMCA method was applied for preprocessed selected spectral data (250-399 nm). The PCA data showed that GIs coffee with different botanical and geographical indications can be well separated. The SIMCA classification was accepted with 100 % of correct classification (100 % CC). This dataset demonstrated the potential use of UV spectroscopy with chemometrics to perform simple and affordable authentication of Indonesian specialty ground roasted coffee with different botanical and geographical indications (GIs).
Keywords: Food authentication; Geographical indications; PCA; SIMCA; Specialty coffee; Spectral data; UV spectroscopy supervised classification.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Director General of Intellectual Property, Geographic Indications. http://e-book.dgip.go.id/indikasi-geografis/, 2020 (accessed 24 April 2020).
-
- Suhandy D., Yulia M. Peaberry coffee discrimination using UV-visible spectroscopy combined with SIMCA and PLS-DA. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017;(20):S331–S339. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2017.1296861. - DOI
-
- Souto U.T.C.P., Pontes M.J.C., Silva E.C., Galvão R.K.H., Araújo M.C.U., Sanches F.A.C., Cunha F.A.S., Oliveira M.S.R. UV–Vis spectrometric classification of coffees by SPA–LDA. Food Chem. 2010;(119):368–371. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.05.078. - DOI
-
- Shawky E., Abu El-Khair R.A., Selim D.A. NIR spectroscopy-multivariate analysis for rapid authentication, detection and quantification of common plant adulterants in saffron (Crocus sativus L.) stigmas. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020;(122) doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109032. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

