Targeting ferroptosis: New perspectives of Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of diabetes and its complications
- PMID: 38076182
- PMCID: PMC10709212
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22250
Targeting ferroptosis: New perspectives of Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of diabetes and its complications
Abstract
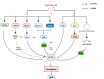
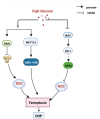
Ferroptosis is a non-apoptotic mode of cell death. A large number of studies have confirmed that ferroptosis plays a vital role in the occurrence and development of diabetes and diabetic complications. Previous studies have found that Chinese herbal medicines have very promising results in the prevention and treatment of diabetes and diabetic complications, and some of these herbs or herbal natural compounds may act via the inhibition of ferroptosis. In this review, we summarized the relationship between ferroptosis and diabetes and diabetic complications, and discussed its molecular mechanisms. We also reviewed the published studies of herbal medicines or herbal natural compounds that improved diabetes or diabetic complications via the ferroptosis pathway. In addition, we are trying to provide new insights for better treatment of diabetes and diabetic complications with Chinese herbal medicine and its herbal compounds.
Keywords: Chinese herbal medicine; Diabetes; Diabetic complications; Ferroptosis; Natural compounds.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Tian J., Jin D., Bao Q., et al. Evidence and potential mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21(8):1801–1816. - PubMed
-
- Kumar S., Mittal A., Babu D., et al. Herbal medicines for diabetes management and its secondary complications. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2021;17(4):437–456. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

