Misdiagnosis of the acute phase of undifferentiated arthritis as pyogenic arthritis: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 38076190
- PMCID: PMC10709495
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22631
Misdiagnosis of the acute phase of undifferentiated arthritis as pyogenic arthritis: A case report and literature review
Abstract
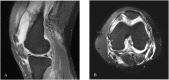
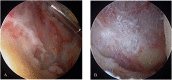
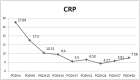
Undifferentiated arthritis is a disease that clinically presents with symptoms and signs of inflammatory arthritis but does not meet the specific diagnostic criteria of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or spondyloarthropathy. Here, we report our experience with a patient whose diagnosis of RA was delayed due to a lack of evidence for RA. The patient complained of knee joint swelling and pain, but the clinical features did not match those of typical pyogenic arthritis. Because infection could not be completely ruled out, the patient was treated for pyogenic arthritis using arthroscopic synovectomy and antibiotics. However, the pain was not relieved and the rheumatologist suggested a diagnosis of undifferentiated monoarthritis, which is an early stage of RA. The pain eventually spread to other joints, leading to the diagnosis of RA, approximately two months after the initial visit. Considering undifferentiated arthritis and making appropriate differential diagnoses is important to avoid unnecessary treatments such as surgery or prolonged antibiotic use. Clinical relevance: Awareness of the possibility of undifferentiated monoarthritis, an early stage of RA, may be helpful in treating patients with recurrent knee effusion.
Keywords: Knee joint; Pyogenic arthritis; Rheumatoid arthritis; Undifferentiated arthritis.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Siva C., Velazquez C., Mody A., Brasington R. Diagnosing acute monoarthritis in adults: a practical approach for the family physician. Am. Fam. Physician. 2003;68:83–92. - PubMed
-
- Thiery J. Arthroscopic drainage in septic arthritides of the knee: a multicenter study. Arthroscopy. 1989;5:65–69. - PubMed
-
- Vincent G.M., Amirault J.D. Clinical orthopaedics and related research; 1990. Septic Arthritis in the Elderly; pp. 241–245. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

