Acne vulgaris: A review of the pathophysiology, treatment, and recent nanotechnology based advances
- PMID: 38076662
- PMCID: PMC10709101
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101578
Acne vulgaris: A review of the pathophysiology, treatment, and recent nanotechnology based advances
Abstract
Background: Globally, Acne Vulgaris is a widespread, chronic inflammatory condition of the pilosebaceous follicles. Acne is not fatal, but depending on its severity, it can leave the sufferer with scars, irritation, and significant psychological effects (including depression). In the current review, we have included various factors for acne and their treatment explained. It also narrated the current medicament and the new investigation dosage forms with clinical phases information provided.
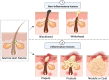
Main body of the abstract: Acne's pathophysiology involves four important factors: excessive sebum production, hyperkeratinization of pilosebaceous follicles, hyperproliferation of propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), and inflammation. Identifying both inflammatory (Papule, pustule, nodule, and cyst) and non-inflammatory (black heads, white heads) acne lesions is necessary for diagnosing and treating acne vulgaris.
Short conclusion: In this review, traditional therapy approaches such as topical (i.e., retinoids and antibiotics), systemic (i.e., retinoids, antibiotics, and hormonal), and physical therapies are briefly discussed. In addition, we highlight the issues posed by P. acne's resistance to the antibiotics used in commercially available medications and the necessity for novel therapeutic techniques. Finally, we examined a few innovative acne therapies pending clinical trial approval and commercial acne medications.
Keywords: Acne inflammation; Acne pathogenesis; Acne treatment; Acne vulgaris; Oral antibiotics; Systemic; Topical retinoids.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. Acknowlegement Dr Raghvendra A Bohara wants to acknowledge Science Foundation Ireland (SFI), co-funded under the European Regional Development Fund under Grant number 13/RC/2073_P2
Figures


References
-
- Maddiboyina B., Jhawat V., Ramesh K., Balaji M. A review on nanoparticle based herbal remedies for the management of alopecia. 2020;12:1–17.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

