This is a preprint.
RNA polymerase II transcription with partially assembled TFIID complexes
- PMID: 38076793
- PMCID: PMC10705246
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.27.567046
RNA polymerase II transcription with partially assembled TFIID complexes
Abstract
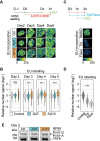
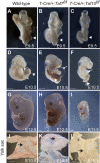
The recognition of core promoter sequences by the general transcription factor TFIID is the first step in the process of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) transcription initiation. Metazoan holo-TFIID is composed of the TATA binding protein (TBP) and of 13 TBP associated factors (TAFs). Inducible Taf7 knock out (KO) results in the formation of a Taf7-less TFIID complex, while Taf10 KO leads to serious defects within the TFIID assembly pathway. Either TAF7 or TAF10 depletions correlate with the detected TAF occupancy changes at promoters, and with the distinct phenotype severities observed in mouse embryonic stem cells or mouse embryos. Surprisingly however, under either Taf7 or Taf10 deletion conditions, TBP is still associated to the chromatin, and no major changes are observed in nascent Pol II transcription. Thus, partially assembled TFIID complexes can sustain Pol II transcription initiation, but cannot replace holo-TFIID over several cell divisions and/or development.
Keywords: RNA polymerase II; TAF10; TAF7; TATA binding protein (TBP); TBP-associated factors (TAFs); TFIID; assembly; embryonic stem cells (ESCs); mass spectrometry; mouse; nascent transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Vermeulen M., Mulder K.W., Denissov S., Pijnappel W.W.M.P., Schaik F.M.A. van, Varier R.A., Baltissen M.P.A., Stunnenberg H.G., Mann M., and Timmers H.T.M. (2007). Selective anchoring of TFIID to nucleosomes by trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 4. Cell 131, 58–69. 10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jacq X., Brou C., Lutz Y., Davidson I., Chambon P., and Tora L. (1994). Human TAFII30 is present in a distinct TFIID complex and is required for transcriptional activation by the estrogen receptor. Cell 79, 107–117. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
