This is a preprint.
Decoding functional hematopoietic progenitor cells in the adult human lung
- PMID: 38077002
- PMCID: PMC10705601
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3576483/v2
Decoding functional hematopoietic progenitor cells in the adult human lung
Update in
-
Decoding functional hematopoietic progenitor cells in the adult human lung.Blood. 2025 May 1;145(18):1975-1986. doi: 10.1182/blood.2024027884. Blood. 2025. PMID: 40014797 Free PMC article.
Abstract
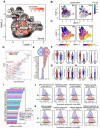
The bone marrow is the main site of blood cell production in adults, however, rare pools of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells with self-renewal and differentiation potential have been found in extramedullary organs. The lung is primarily known for its role in gas exchange but has recently been described as a site of blood production in mice. Here, we show that functional hematopoietic precursors reside in the extravascular spaces of the human lung, at a frequency similar to the bone marrow, and are capable of proliferation and engraftment. The organ-specific gene signature of pulmonary and medullary CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors indicates greater baseline activation of immune, megakaryocyte/platelet and erythroid-related pathways in lung progenitors. Spatial transcriptomics mapped blood progenitors in the lung to a vascular-rich alveolar interstitium niche. These results identify the lung as a pool for uniquely programmed blood stem and progenitor cells with the potential to support hematopoiesis in humans.
Keywords: Blood and Immune Cell Production; Erythropoeisis; Extramedullary Hematopoeisis; Hematopoeitic stem and progenitor cells; Stem Cell Biology; Stem Cell Transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

