Elevated monocyte HLA-DR in pediatric secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a retrospective study
- PMID: 38077325
- PMCID: PMC10704813
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1286749
Elevated monocyte HLA-DR in pediatric secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a retrospective study
Abstract
Introduction: Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a life-threatening condition, and its diagnosis may be challenging. In particular, some cases show close similarities to sepsis (fever, organ failure, and high ferritin), but their treatment, while urgent, differ: prompt broad-spectrum antibiotherapy for sepsis and immunosuppressive treatment for HLH. We questioned whether monocyte human leucocyte antigen (mHLA)-DR could be a diagnostic marker for secondary HLH (sHLH).
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed data from patients with a sHLH diagnosis and mHLA-DR quantification. mHLA-DR data from healthy children and children with septic shock, whose HLA-DR expression is reduced, from a previously published study were also included for comparison.
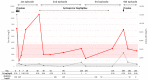
Results: Six patients with sHLH had mHLA-DR quantification. The median level of monocyte mHLA-DR expression in patients with sHLH [79,409 antibodies bound per cell (AB/C), interquartile range (IQR) (75,734-86,453)] was significantly higher than that in healthy children and those with septic shock (29,668 AB/C, IQR (24,335-39,199), and 7,493 AB/C, IQR (3,758-14,659), respectively). Each patient with sHLH had a mHLA-DR higher than our laboratory normal values. Four patients had a second mHLA-DR sampling 2 to 4 days after the initial analysis and treatment initiation with high-dose corticosteroids; for all patients, mHLA-DR decreased to within or close to the normal range. One patient with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis had repeated mHLA-DR measurements over a 200-day period during which she underwent four HLH episodes. mHLA-DR increased during relapses and normalized after treatment incrementation.
Conclusion: In this small series, mHLA-DR was systematically elevated in patients with sHLH. Elevated mHLA-DR could contribute to sHLH diagnosis and help earlier distinction with septic shock.
Keywords: cytokine storm; hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; lymphocyte activation; macrophage activation syndrome; monocyte HLA-DR.
Copyright © 2023 Raimbault, Monneret, Gossez, Venet, Belot, Zekre, Remy and Javouhey.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- Jordan MB, Allen CE, Greenberg J, Henry M, Hermiston ML, Kumar A, et al. . Challenges in the diagnosis of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Recommendations from the North American Consortium for Histiocytosis (NACHO). Pediatr Blood Cancer (2019) 66(11):e27929. doi: 10.1002/pbc.27929 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

