Cytogenotoxic potential and toxicity in adult Danio rerio (zebrafish) exposed to chloramine T
- PMID: 38077413
- PMCID: PMC10702335
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.16452
Cytogenotoxic potential and toxicity in adult Danio rerio (zebrafish) exposed to chloramine T
Abstract
Background: Chloramine-T (CL-T) is a synthetic sodium salt used as a disinfectant in fish farms to combat bacterial infections in fish gills and skin. While its efficacy in pathogen control is well-established, its reactivity with various functional groups has raised concerns. However, limited research exists on the toxicity of disinfection by-products to aquatic organisms. Therefore, this study aims to assess the sublethal effects of CL-T on adult zebrafish by examining biomarkers of nucleus cytotoxicity and genotoxicity, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition, and histopathological changes.
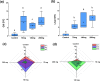
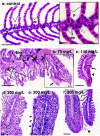
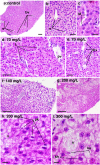
Methods: Male and female adult zebrafish (wildtype AB lineage) specimens were exposed to 70, 140, and 200 mg/L of CL-T and evaluated after 96 h. Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects were evaluated by estimating the frequencies of nuclear abnormalities (NA), micronuclei (MN), and integrated optical density (IOD) of nuclear erythrocytes. Histopathological changes in the gills and liver were assessed using the degree of tissue changes (DTC). AChE activity was measured in brain samples.
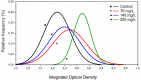
Results and conclusions: At a concentration of 200 mg/L, NA increased, indicating the cytogenotoxic potential of CL-T in adult zebrafish. Morphological alterations in the nuclei were observed at both 70 and 200 mg/L concentrations. Distinct IOD profiles were identified across the three concentrations. There were no changes in AChE activity in adult zebrafish. The DTC scores were high in all concentrations, and histological alterations suggested low to moderate toxicity of CL-T for adult zebrafish.
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase activity; Gill and liver histopathology; Integrated optical density (IOD); Micronucleus test; Nuclear abnormalities.
©2023 Rivero-Wendt et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Carlos Eurico Fernandes is an Academic Editor for PeerJ.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Acute exposure of zebrafish (Danio rerio) adults to psychotria carthagenensis leaf extracts: chemical profile, lack of genotoxicity and histological changes.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2024 Nov;47(6):1358-1368. doi: 10.1080/01480545.2024.2367560. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38953234
-
Effects of Chloramine T on zebrafish embryos malformations associated with cardiotoxicity and neurotoxicity.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2023 Apr 26:1-10. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2023.2205271. Online ahead of print. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2023. PMID: 37185102
-
Silver nanoparticles inhibit the gill Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase and erythrocyte AChE activities and induce the stress response in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio).Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2014 Aug;106:173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.04.001. Epub 2014 May 20. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2014. PMID: 24840880
-
Chloramine-T application for Trichodina sp. in Arapaima gigas juveniles: Acute toxicity, histopathology, efficacy, and physiological effects.Vet Parasitol. 2022 Mar;303:109667. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2022.109667. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Vet Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35124292
-
Micronucleus test and nuclear abnormality assay in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Past, present, and future trends.Environ Pollut. 2021 Dec 1;290:118019. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118019. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Environ Pollut. 2021. PMID: 34670334 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Assessment of Short- and Long-Term Effects of Triadimenol Fungicide on Danio rerio Erythrocytes Using the Micronucleus and Erythrocyte Nuclear Abnormality Assays.Toxics. 2025 Mar 11;13(3):199. doi: 10.3390/toxics13030199. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40137526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agoba E, Adu F, Agyare C, Boamah V. Antibiotic use and practices in selected fish farms in the Ashanti Region of Ghana. Journal of Infectious Diseases and Treatment. 2017;03:1–6. doi: 10.21767/2472-1093.100036. - DOI
-
- Alidadi Soleiman T, Sattari A, Kheirandish R, Sharifpour I. Safety evaluation of chloramine—T on ornamental zebra fish (Danio rerio) using LC50 calculation and organ pathology. Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences. 2017;16:26–37.
-
- Bahadir T, Çelebi H, Şimşek İ, Tulun Ş. Antibiotic applications in fish farms and environmental problems. Turkish Journal of Engineering. 2019;3:60–67. doi: 10.31127/tuje.452921. - DOI
-
- Bernet D, Schmidt-Posthaus H, Meier W, Burkhardt-Holm P, Wahli T. Histopathology in fish: proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. The Journal of Fish Disease. 2001;22:25–34. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2761.1999.00134.x. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

