Understanding the black-box: towards interpretable and reliable deep learning models
- PMID: 38077598
- PMCID: PMC10702969
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1629
Understanding the black-box: towards interpretable and reliable deep learning models
Abstract
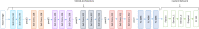
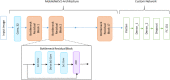
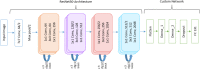
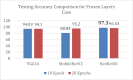
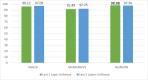
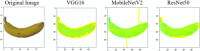
Deep learning (DL) has revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence by providing sophisticated models across a diverse range of applications, from image and speech recognition to natural language processing and autonomous driving. However, deep learning models are typically black-box models where the reason for predictions is unknown. Consequently, the reliability of the model becomes questionable in many circumstances. Explainable AI (XAI) plays an important role in improving the transparency and interpretability of the model thereby making it more reliable for real-time deployment. To investigate the reliability and truthfulness of DL models, this research develops image classification models using transfer learning mechanism and validates the results using XAI technique. Thus, the contribution of this research is twofold, we employ three pre-trained models VGG16, MobileNetV2 and ResNet50 using multiple transfer learning techniques for a fruit classification task consisting of 131 classes. Next, we inspect the reliability of models, based on these pre-trained networks, by utilizing Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations, the LIME, a popular XAI technique that generates explanations for the predictions. Experimental results reveal that transfer learning provides optimized results of around 98% accuracy. The classification of the models is validated on different instances using LIME and it was observed that each model predictions are interpretable and understandable as they are based on pertinent image features that are relevant to particular classes. We believe that this research gives an insight for determining how an interpretation can be drawn from a complex AI model such that its accountability and trustworthiness can be increased.
Keywords: Deep learning; Explainable AI; Pre-trained models; Transfer learning.
©2023 Qamar and Bawany.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Alzubaidi L, Zhang J, Humaidi AJ, Al-Dujaili A, Duan Y, Al-Shamma O, Santamaría J, Fadhel MA, Al-Amidie M, Farhan L. Review of deep learning: concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. Journal of Big Data. 2021;8(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s40537-021-00444-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azarmdel H, Jahanbakhshi A, Mohtasebi SS, Rosado Muñoz A. Evaluation of image processing technique as an expert system in mulberry fruit grading based on ripeness level using artificial neural networks (ANNs) and support vector machine (SVM) Postharvest Biology and Technology. 2020;166:111201. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111201. - DOI
-
- Bhattacharjee S, Hwang YB, Ikromjanov K, Sumon RI, Kim HC, Choi HK. An explainable computer vision in histopathology: techniques for interpreting black box model. 4th international conference on artificial intelligence in information and communication, ICAIIC 2022—proceedings; 2022. pp. 392–398. - DOI
-
- Dastin J. Ethics of data and analytics. Auerbach Publications; 2022. Amazon scraps secret AI recruiting tool that showed bias against women; pp. 296–299.
-
- Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L-J, Li K, Fei-Fei L. ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2009. pp. 248–255. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
