A single synthetic lipid antigen for improved serological diagnosis of Buruli ulcer
- PMID: 38077720
- PMCID: PMC10703138
- DOI: 10.5588/pha.23.0038
A single synthetic lipid antigen for improved serological diagnosis of Buruli ulcer
Abstract
Setting: The diagnosis of Buruli ulcer (BU) is frequently made by experienced health workers in rural regions. This leads to long turnaround times to confirm the diagnosis as it requires specialised laboratory infrastructure to perform confirmatory testing.
Background: Given the lack of success with protein antigens to detect BU in human sera, the aim of this study was to evaluate a range of single synthetic lipid antigens using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The ELISA system used was initially developed to detect TB using single synthetic lipid antigens.
Methods: Thirty polymerase chain reaction (PCR) positive BU samples and 30 PCR-negative healthy contact samples collected from Asante Akim North and Ahafo Ano North Districts, Ghana, that are endemic for BU between 2013 and 2016 were used to evaluate the synthetic lipid antigen ELISA. A Quantikine ELISA was also conducted on a randomly blinded sub-set of 30 samples.
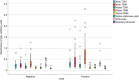
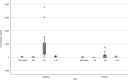
Results: The synthetic lipid ELISA evaluated here outperforms all other ELISA tests using protein antigens to detect BU to date and has shown potential as a fast (2 h) test for BU which may be adapted for use at the point of care. A sensitivity of 63% and specificity of 80% was observed for 30 BU-positive and 30 BU-negative samples, with significantly reduced interleukin-8 (IL-8) levels in a subset of patients with BU.
Conclusion: A single lipid was shown for the first time to have the ability to distinguish between PCR-positive BU and negative sera using ELISA. The low lipid antibody load detected may be a result of immune suppression caused by the presence of mycolactone in patients with BU, given that levels of IL-8 were significantly reduced in patients with BU compared to the control serum samples.
Keywords: BU; TDM; cord factor; lipid antigen; mycolic acid; point-of-care diagnosis.
© 2023 The Union.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization Fifty-seventh World Health Assembly. Geneva: Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; May 2004. 2004. Resolution WHA57.1 Surveillance and control of Mycobacterium ulcerans disease (Buruli ulcer) pp. 17–22. Resolutions and decisions.
-
- Tschakert P, et al. Situated knowledge of pathogenic landscapes in Ghana: understanding the emergence of Buruli ulcer through qualitative analysis. Soc Sci Med. 2016;150:160–171. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organisation Buruli Ulcer Factsheet. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2017.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

