Accuracy of Hip Pericapsular Nerve Block (PENG) without Ultrasound Aid in Patients with Hip Pain
- PMID: 38077758
- PMCID: PMC10708984
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-1776909
Accuracy of Hip Pericapsular Nerve Block (PENG) without Ultrasound Aid in Patients with Hip Pain
Abstract
Objective To describe and evaluate the accuracy of the pericapsular nerve group (PENG) block technique with no ultrasound guidance. Method Series of 40 infiltrations in patients with hip pain undergoing outpatient follow-up in the hip surgery group or admitted to the emergency room from a hospital in São Paulo, SP, Brazil. The hip PENG technique was guided by palpable anatomical pelvic structures, with no ultrasound orientation for needle positioning, using the equipment only to check the correct location after an unguided puncture. Results In the 40 hips infiltrated from 35 patients with a mean age of 59.2 years, the success rate was 85%. Among the mispositioned cases, 71.4% occurred in the first 13 applications and 28.6% in the subsequent 27 applications. In all patients, the neurovascular bundle was in the medial third of the pen-made demarcation. Even in cases with a failed needle location, the distance from the neurovascular bundle was safe. A single adverse effect occurred, with spontaneous improvement of the femoral nerve apraxia within two days. Conclusion Unguided PENG block is a viable technique for a physician knowledgeable about its application in services with no ultrasound availability.
Keywords: analgesia; anesthesia; hip fractures; nerve block; pain management.
Sociedade Brasileira de Ortopedia e Traumatologia. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflito de Interesses Os autores declaram inexistência de Conflito de Interesses na realização deste trabalho.
Figures








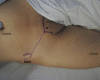



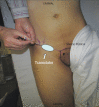

References
-
- Girón-Arango L, Peng P WH, Chin K J, Brull R, Perlas A. Pericapsular Nerve Group (PENG) Block for Hip Fracture. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2018;43(08):859–863. - PubMed
-
- Orozco S, Muñoz D, Jaramillo S, Herrera A M. Pericapsular Nerve Group (PENG) block for perioperative pain control in hip arthroscopy. J Clin Anesth. 2020;59:3–4. - PubMed
-
- Del Buono R, Padua E, Pascarella G, Soare C G, Barbara E. Continuous PENG block for hip fracture: a case series. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2020;45(10):835–838. - PubMed
-
- Morrison C, Brown B, Lin D Y, Jaarsma R, Kroon H.Analgesia and anesthesia using the pericapsular nerve group block in hip surgery and hip fracture: a scoping review[published correction appears in Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2022 May;47(5):e1]Reg Anesth Pain Med 20214602169–175. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

