Fibroma of the Patellar Tendon Sheath: A New Paradigm
- PMID: 38077770
- PMCID: PMC10708965
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1722594
Fibroma of the Patellar Tendon Sheath: A New Paradigm
Abstract
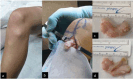
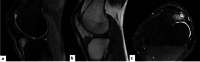
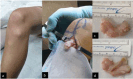
The authors present a case of fibroma of the tendon sheath with intra-articular location in the knee, more specifically in the infrapatellar fat; with this specific location, this is the fourth case described of an entity that rarely affects large joints. Clinical and epidemiological aspects, but especially the imaging findings on magnetic resonance imaging scans, are essential for the differential and definitive diagnosis, which was nevertheless established only after a histological study of the excised mass by miniarthrotomy.
Keywords: fibroma of tendon sheath; intra-articular fibroma; knee; patellar tendon.
Sociedade Brasileira de Ortopedia e Traumatologia. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflito de Interesses Os autores declaram não haver conflito de interesses.
Figures



References
-
- Pinar H, Ozkan M, Ozaksoy D, Pabuççuoğlu U, Akseki D, Karaoğlan O. Intraarticular fibroma of the tendon sheath of the knee. Arthroscopy. 1995;11(05):608–611. - PubMed
-
- Geschickter C F, Copeland M M. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott Co; 1949. Tumors of bone.
-
- Aynaci O, Kerimoglu S, Ozturk C, Saracoglu M, Yildiz K. Intraarticular fibroma of the tendon sheath arising from the infrapatellar fat pad in the knee joint. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(03):291–294. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

