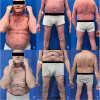
A Case of Erythrodermic Psoriasis Successfully Treated with Risankizumab
- PMID: 38077922
- PMCID: PMC10710257
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S447123
A Case of Erythrodermic Psoriasis Successfully Treated with Risankizumab
Erratum in
-
Erratum: A Case of Erythrodermic Psoriasis Successfully Treated with Risankizumab [Corrigendum].Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024 Jun 18;17:1447-1448. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S482737. eCollection 2024. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38911339 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory cutaneous disease, affecting up to 3% of the worldwide population. Several clinical phenotypes can be distinguished. Among these, erythrodermic psoriasis (EP) is a rare and severe variant (less than 3% of cases), characterized by severe generalized erythema and scaling affecting at least 90% of the body surface area. EP is often a life-threatening condition, since several systemic symptoms (tachycardia, fever, fatigue, lymphadenopathy, dehydration, serum electrolyte disturbances) can be associated. Thus, a prompt and appropriate treatment is mandatory. Unfortunately, EP treatment is challenging. Indeed, the reduced prevalence of EP makes clinical trials feasibility difficult, leading to the absence of established guidelines. So, the treatment of EP is often derived from moderate-to-severe psoriasis management which relies on the use of conventional systemic drugs (cyclosporine, dimethyl fumarate, methotrexate, retinoids) and biologic agents. However, conventional systemic drugs are often contraindicated for patients' comorbidities, or their use is characterized by reduced efficacy and various adverse events (AEs). The recent development of biologic drugs, which showed excellent results in terms of effectiveness and safety in plaque psoriasis, made these drugs an ideal weapon in EP management, despite their use in EP is still off-label. Among these, risankizumab, a humanized immunoglobulin G1 monoclonal antibody targeting the p19 subunit of the IL23, is one of the latest biologics approved for the management of moderate-to-severe psoriasis. Herein, we reported the first case of a caucasian patient affected by EP successfully treated with risankizumab, reaching PASI100 response after 16 weeks of treatment, without experiencing AEs.
Keywords: erythrodermic psoriasis; risankizumab; treatment.
© 2023 Megna et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources