The Improved Kidney Risk Score in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis for Clinical Practice and Trials
- PMID: 38082490
- PMCID: PMC10914211
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.0000000000000274
The Improved Kidney Risk Score in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis for Clinical Practice and Trials
Abstract
Significance statement: Reliable prediction tools are needed to personalize treatment in ANCA-associated GN. More than 1500 patients were collated in an international longitudinal study to revise the ANCA kidney risk score. The score showed satisfactory performance, mimicking the original study (Harrell's C=0.779). In the development cohort of 959 patients, no additional parameters aiding the tool were detected, but replacing the GFR with creatinine identified an additional cutoff. The parameter interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy was modified to allow wider access, risk points were reweighted, and a fourth risk group was created, improving predictive ability (C=0.831). In the validation, the new model performed similarly well with excellent calibration and discrimination ( n =480, C=0.821). The revised score optimizes prognostication for clinical practice and trials.
Background: Reliable prediction tools are needed to personalize treatment in ANCA-associated GN. A retrospective international longitudinal cohort was collated to revise the ANCA renal risk score.
Methods: The primary end point was ESKD with patients censored at last follow-up. Cox proportional hazards were used to reweight risk factors. Kaplan-Meier curves, Harrell's C statistic, receiver operating characteristics, and calibration plots were used to assess model performance.
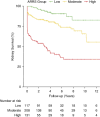
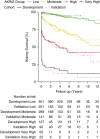
Results: Of 1591 patients, 1439 were included in the final analyses, 2:1 randomly allocated per center to development and validation cohorts (52% male, median age 64 years). In the development cohort ( n =959), the ANCA renal risk score was validated and calibrated, and parameters were reinvestigated modifying interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy allowing semiquantitative reporting. An additional cutoff for kidney function (K) was identified, and serum creatinine replaced GFR (K0: <250 µ mol/L=0, K1: 250-450 µ mol/L=4, K2: >450 µ mol/L=11 points). The risk points for the percentage of normal glomeruli (N) and interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (T) were reweighted (N0: >25%=0, N1: 10%-25%=4, N2: <10%=7, T0: none/mild or <25%=0, T1: ≥ mild-moderate or ≥25%=3 points), and four risk groups created: low (0-4 points), moderate (5-11), high (12-18), and very high (21). Discrimination was C=0.831, and the 3-year kidney survival was 96%, 79%, 54%, and 19%, respectively. The revised score performed similarly well in the validation cohort with excellent calibration and discrimination ( n =480, C=0.821).
Conclusions: The updated score optimizes clinicopathologic prognostication for clinical practice and trials.
Copyright © 2023 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
I. Bajema reports Consultancy: Aurinia, Boehringer Ingelheim, CatBio, GSK, Hansa, Novartis, Otsuka, Toleranzia, Vera, and Vifor; Advisory or Leadership Role: C3 Glomerulopathy review board (Novartis, The Netherlands) and Glomerular Disease Council (Vifor Pharma); and Other Interests or Relationships: Director of Bajema Institute of Pathology, Past President of Renal Pathology Society, and Vice-President of European Vasculitis Society (EUVAS). S. Bate reports Employer: IQVIA and Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust. B. Brilland reports Honoraria: CSL Vifor and Sanofi. S.R. Brix reports Honoraria: Vifor; Advisory or Leadership Role: Vifor; and Speakers Bureau: Vifor. N. Brown reports Honoraria: Vifor; and Other Interests or Relationships: Chair of Education Committee, United Kingdom and Ireland Vasculitis Society. N. Dhaun reports Consultancy: Travere Pharmaceutical; Research Funding: Pfizer and Travere Pharma; and Advisory or Leadership Role: Travere. A. Dhaygude reports Honoraria: Speaker fees for AstraZenica and Advisory or Leadership Role: Vifor Pharma. G. Duruvu reports Consultancy: Amgen, Aurinia, Calliditas, ChemoCentryx, GSK, and Otsuka. D. Ilyas reports Research Funding: PhD Research Projects funded by Invizius Limited. D.R.W. Jayne reports Consultancy: AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Chemocentryx, Chinook, GSK, Novartis, Otsuka, Roche/Genentech, Takeda, and Vifor; Ownership Interest: Aurinia; Research Funding: GSK, Roche/Genentech, and Vifor; Honoraria: GSK, Otsuka, and Vifor; Advisory or Leadership Role: Aurinia; and Speakers Bureau: GSK and Vifor. J.C. Jennette reports Employer: Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc. R.B. Jones reports Research Funding: GSK and Roche; Honoraria: Roche; and Advisory or Leadership Role: Advisory boards for CSL Vifor and GSK. J.S. Lees reports Honoraria: AstraZeneca. M.A. Little reports Research Funding: CSL Vifor; Patents or Royalties: Euroimmun; and Speakers Bureau: CSL Vifor. S.P. McAdoo reports Consultancy: CSL Vifor and GSK; Research Funding: AstraZeneca and Therini Bio; Honoraria: Celltrion, Rigel Pharmaceuticals, and ThermoFisher Scientific; and Advisory or Leadership Role: Co-chair United Kingdom and Ireland Vasculitis Society (unpaid). J.M. Mejía-Vilet reports Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Novartis, and Roche. E. Nic an Riogh reports Research Funding: Health Research Board Ireland and Wellcome (203930/B/16/Z), the Health Service Executive, National Doctors Training and Planning and the Health and Social Care, Research and Development Division, Northern Ireland supports the Irish Clinical Academic Training (ICAT) Program, of which Dr. E. Nic an Riogh is a Wellcome-HRB Irish Clinical Academic Training (ICAT) Fellow. C.D. Pusey reports Consultancy: Alentis and Vifor; Honoraria: Amgen and Med Update Europe; and Advisory or Leadership Role:
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

