The effect of hair type and texture on electroencephalography and event-related potential data quality
- PMID: 38084752
- PMCID: PMC10922334
- DOI: 10.1111/psyp.14499
The effect of hair type and texture on electroencephalography and event-related potential data quality
Abstract
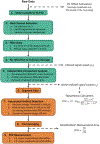
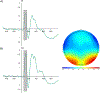
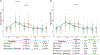
Research utilizing event-related potential (ERP) methods is generally biased with regard to sample representativeness. Among the myriad of factors that contribute to sample bias are researchers' assumptions about the extent to which racial differences in hair texture, volume, and style impact electrode placement, and subsequently, study eligibility. The current study examines these impacts using data collected from n = 213 individuals ages 17-19 years, and offers guidance on collection of ERP data across the full spectrum of hair types. Individual differences were quantified for hair texture using a visual scale, and for hair volume by measuring the amount of gel used in cap preparation. Electroencephalography data quality was assessed with multiple metrics at the preprocessing, post-processing, and variable generation stages. Results indicate that hair volume is associated with small, but systematic differences in signal quality and signal amplitude. Such differences are highly problematic as they could be misattributed to cognitive differences among groups. However, inclusion of gel volume as a covariate to account for individual differences in hair volume significantly reduced, and in most cases eliminated, group differences. We discuss strategies for overcoming real and perceived technical barriers for researchers seeking to achieve greater inclusivity and representativeness in ERP research.
Keywords: EEG; diversity; ethnicity; hair style; race; representation.
© 2023 The Authors. Psychophysiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Society for Psychophysiological Research.
Figures

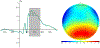
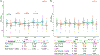
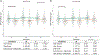
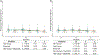
References
-
- Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, & Walker S (2015). Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67(1), 1–48. 10.18637/jss.v067.i01 - DOI
-
- Broyd SJ, Richards HJ, Helps SK, Chronaki G, Bamford S, & Sonuga-Barke EJS (2012). An electrophysiological monetary incentive delay (e-MID) task: A way to decompose the different components of neural response to positive and negative monetary reinforcement. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 209(1), 40–49. 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2012.05.015 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

