Embedded macrophages induce intravascular coagulation in 3D blood vessel-on-chip
- PMID: 38085384
- PMCID: PMC10716057
- DOI: 10.1007/s10544-023-00684-w
Embedded macrophages induce intravascular coagulation in 3D blood vessel-on-chip
Abstract
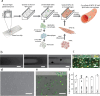
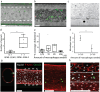
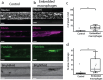
Macrophages are innate immune cells that prevent infections and help in wound healing and vascular inflammation. While these cells are natural helper cells, they also contribute to chronic diseases, e.g., by infiltrating the endothelial layer in early atherosclerosis and by promoting vascular inflammation. There is a crosstalk between inflammatory pathways and key players in thrombosis, such as platelets and endothelial cells - a phenomenon known as 'thromboinflammation'. The role of the embedded macrophages in thromboinflammation in the context of vascular disease is incompletely understood. Blood vessels-on-chips, which are microfluidic vascular cell culture models, have been used extensively to study aspects of vascular disease, like permeability, immune cell adhesion and thrombosis. Blood perfusion assays in blood vessel-on-chip models benefit from multiple unique aspects of the models, such as control of microvessel structure and well-defined flow patterns, as well as the ability to perform live imaging. However, due to their simplified nature, blood vessels-on-chip models have not yet been used to capture the complex cellular crosstalk that is important in thromboinflammation. Using induced pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells and polarized THP-1 monocytes, we have developed and systematically set up a 3D blood vessel-on-chip with embedded (lipid-laden) macrophages, which is created using sequential cell seeding in viscous finger patterned collagen hydrogels. We have set up a human whole blood perfusion assay for these 3D blood vessels-on-chip. An increased deposition of fibrin in the blood vessel-on-chip models containing lipid-laden macrophages was observed. We anticipate the future use of this advanced vascular in vitro model in drug development for early atherosclerosis or aspects of other vascular diseases.
Keywords: Macrophage; Organ-on-chip; THP-1; Thromboinflammation; Vessel-on-chip; hiPSC-EC.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blood-perfused Vessels-on-Chips stimulated with patient plasma recapitulate endothelial activation and microthrombosis in COVID-19.Lab Chip. 2025 Mar 25;25(7):1787-1800. doi: 10.1039/d4lc00848k. Lab Chip. 2025. PMID: 40034052 Free PMC article.
-
Organ-on-chips made of blood: endothelial progenitor cells from blood reconstitute vascular thromboinflammation in vessel-chips.Lab Chip. 2019 Jul 23;19(15):2500-2511. doi: 10.1039/c9lc00469f. Lab Chip. 2019. PMID: 31246211 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve pathology of microangiopathy and thromboinflammation in hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024 Jan;11(1):30-44. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51930. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024. PMID: 37902278 Free PMC article.
-
Dangerous liaisons: complement, coagulation, and kallikrein/kinin cross-talk act as a linchpin in the events leading to thromboinflammation.Immunol Rev. 2016 Nov;274(1):245-269. doi: 10.1111/imr.12471. Immunol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27782319 Review.
-
Platelet Versus Megakaryocyte: Who Is the Real Bandleader of Thromboinflammation in Sepsis?Cells. 2022 Apr 30;11(9):1507. doi: 10.3390/cells11091507. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563812 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NebulaPlate: a droplet microfluidic platform to analyze platelet aggregation.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Mar 5;23(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03212-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40045357 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-perfused Vessels-on-Chips stimulated with patient plasma recapitulate endothelial activation and microthrombosis in COVID-19.Lab Chip. 2025 Mar 25;25(7):1787-1800. doi: 10.1039/d4lc00848k. Lab Chip. 2025. PMID: 40034052 Free PMC article.
-
THP-1 Macrophages Limit Neutrophil Transendothelial Migration in a Model Infection.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2024 Jul 20;17(4):279-293. doi: 10.1007/s12195-024-00813-2. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2024. PMID: 39372553 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic Gastrointestinal Cell Culture Technologies-Improvements in the Past Decade.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Sep 19;14(9):449. doi: 10.3390/bios14090449. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39329824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organ-on-chip platforms for nanoparticle toxicity and efficacy assessment: Advancing beyond traditional in vitro and in vivo models.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jul 4;33:102053. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102053. eCollection 2025 Aug. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40688675 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barrile R, van der Meer AD, Park H, Fraser JP, Simic D, Teng F, Conegliano D, Nguyen J, Jain A, Zhou M, Karalis K, Ingber DE, Hamilton GA, Otieno MA. Organ-on-Chip recapitulates thrombosis induced by an anti-CD154 monoclonal antibody: Translational potential of advanced microengineered systems. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018;104(6):1240–1248. doi: 10.1002/cpt.1054. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

