Transcriptional Plasticity Drives IMiD and p300 Inhibitor Resistance in Multiple Myeloma
- PMID: 38085608
- PMCID: PMC10772544
- DOI: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-23-0223
Transcriptional Plasticity Drives IMiD and p300 Inhibitor Resistance in Multiple Myeloma
Abstract
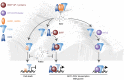
In this issue of Blood Cancer Discovery, Neri, Barwick, and colleagues and Welsh, Barwick, and colleagues performed RNA sequencing, chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing, assay for transposase-accessible chromatin using sequencing, and genetic studies to characterize the underlying mechanisms of immunomodulatory drug (IMiD) resistance in multiple myeloma. They demonstrated that IMiD resistance is driven by sustained expression of MYC and IRF4 via transcriptional plasticity that involves induction of ETV4 and BATF proteins, the binding of these proteins to their super-enhancers, and the recruitment of BRD4 and p300. Finally, these studies suggest IMiD and p300 inhibitor combination as a promising therapeutic strategy in multiple myeloma. See related article by Neri, Barwick, et al., p. 56 (9). See related article by Welsh, Barwick, et al., p. 34 (10).
©2023 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Comment on
-
Transcriptional Heterogeneity Overcomes Super-Enhancer Disrupting Drug Combinations in Multiple Myeloma.Blood Cancer Discov. 2024 Jan 8;5(1):34-55. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-23-0062. Blood Cancer Discov. 2024. PMID: 37767768 Free PMC article.
-
ETV4-Dependent Transcriptional Plasticity Maintains MYC Expression and Results in IMiD Resistance in Multiple Myeloma.Blood Cancer Discov. 2024 Jan 8;5(1):56-73. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-23-0061. Blood Cancer Discov. 2024. PMID: 37934799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cowan AJ, Green DJ, Kwok M, Lee S, Coffey DG, Holmberg LA, et al. . Diagnosis and management of multiple myeloma: a review. JAMA 2022;327:464–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

