Cortiva versus AlloDerm in Prepectoral and Partial Submuscular Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 38085977
- PMCID: PMC11412571
- DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000011244
Cortiva versus AlloDerm in Prepectoral and Partial Submuscular Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: Several acellular dermal matrices (ADMs) are used for soft-tissue support in prosthetic breast reconstruction. Little high-level evidence supports the use of one ADM over another. The authors sought to compare Cortiva 1-mm Allograft Dermis with AlloDerm RTU (ready to use), the most studied ADM in the literature.
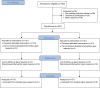
Methods: A single-blinded randomized controlled trial comparing Cortiva with AlloDerm in prepectoral and subpectoral immediate prosthetic breast reconstruction was performed at 2 academic hospitals from March of 2017 to December of 2021. Reconstructions were direct to implant (DTI) or tissue expander (TE). Primary outcome was reconstructive failure, defined as TE explantation before planned further reconstruction, or explantation of DTI reconstructions before 3 months postoperatively. Secondary outcomes were additional complications, patient-reported outcomes (PROs), and cost.
Results: There were 302 patients included: 151 AlloDerm (280 breasts), 151 Cortiva (277 breasts). The majority of reconstructions in both cohorts consisted of TE (62% versus 38% DTI), smooth device (68% versus 32% textured), and prepectoral (80% versus 20% subpectoral). Reconstructive failure was no different between ADMs (AlloDerm 9.3% versus Cortiva 8.3%; P = 0.68). There were no additional differences in any complications or PROs between ADMs. Seromas occurred in 7.6% of Cortiva but 12% of AlloDerm cases, in which the odds of seroma formation were two-fold higher (odds ratio, 1.93 [95% CI, 1.01 to 3.67]; P = 0.047). AlloDerm variable cost was 10% to 15% more than Cortiva, and there were no additional cost differences.
Conclusion: When assessing safety, clinical performance, PROs, and cost, Cortiva is noninferior to AlloDerm in immediate prosthetic breast reconstruction, and may be less expensive, with lower risk of seroma formation.
Clinical question/level of evidence: Therapeutic, I.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Myckatyn receives investigator-initiated grant funding, royalties, and advisory board renumeration from RTI Surgical, and investigator-initiated grant funding from Sientra. Royalties are not derived from the product studied in this article, and Dr. Myckatyn has not ever used the product for which he has received royalties. Dr. Tenenbaum receives consulting fees from NC8, Allergan, and RTI Surgical, and grant funding from Mentor. The remaining authors have no financial interests to report.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7–33. - PubMed
-
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons. 2020 Plastic Surgery Statistics Report: ASPS National Clearinghouse of Plastic Surgery Procedural Statistics. Available at: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2020/plastic-su.... Accessed March 14, 2023.
-
- Albornoz CR, Bach PB, Mehrara BJ, et al. . A paradigm shift in U.S. breast reconstruction: increasing implant rates. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131:15–23. - PubMed
-
- Albornoz CR, Cordeiro PG, Farias-Eisner G, et al. . Diminishing relative contraindications for immediate breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;134:363e–369e. - PubMed
-
- Gamboa-Bobadilla GM. Implant breast reconstruction using acellular dermal matrix. Ann Plast Surg. 2006;56:22–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

