AI-based diagnosis of nuclear cataract from slit-lamp videos
- PMID: 38086904
- PMCID: PMC10716159
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-49563-7
AI-based diagnosis of nuclear cataract from slit-lamp videos
Abstract
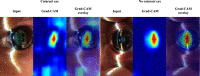
In ophthalmology, the availability of many fundus photographs and optical coherence tomography images has spurred consideration of using artificial intelligence (AI) for diagnosing retinal and optic nerve disorders. However, AI application for diagnosing anterior segment eye conditions remains unfeasible due to limited standardized images and analysis models. We addressed this limitation by augmenting the quantity of standardized optical images using a video-recordable slit-lamp device. We then investigated whether our proposed machine learning (ML) AI algorithm could accurately diagnose cataracts from videos recorded with this device. We collected 206,574 cataract frames from 1812 cataract eye videos. Ophthalmologists graded the nuclear cataracts (NUCs) using the cataract grading scale of the World Health Organization. These gradings were used to train and validate an ML algorithm. A validation dataset was used to compare the NUC diagnosis and grading of AI and ophthalmologists. The results of individual cataract gradings were: NUC 0: area under the curve (AUC) = 0.967; NUC 1: AUC = 0.928; NUC 2: AUC = 0.923; and NUC 3: AUC = 0.949. Our ML-based cataract diagnostic model achieved performance comparable to a conventional device, presenting a promising and accurate auto diagnostic AI tool.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
E.S. is the founder of OUI Inc. and owns stock in OUI Inc. The other authors declare no competing interest associated with this manuscript. OUI Inc. did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Figures




References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Health Estimates 2016: Disease Burden by Cause, Age, Sex, by Country and by Region, 2000–2016 (World Health Organization, 2018).
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

