Cortical microvascular raspberries and ageing: an independent but not exclusive relationship
- PMID: 38087325
- PMCID: PMC10714499
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-023-01700-z
Cortical microvascular raspberries and ageing: an independent but not exclusive relationship
Abstract
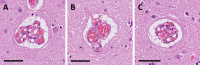
Introduction: Raspberries are cerebral microvascular formations of unknown origin, defined as three or more transversally sectioned vascular lumina surrounded by a common perivascular space. We have previously demonstrated an increased raspberry density in the cortex of patients with vascular dementia and cerebral atherosclerosis, while studies by other authors on overlapping and synonymously defined vascular entities mainly associate them with advancing age. The aim of the present study was to examine the relationship between raspberries and age in a large study sample while including multiple potential confounding factors in the analysis.
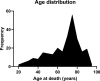
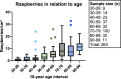
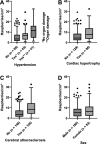
Materials and methods: Our study sample consisted of 263 individuals aged 20-97 years who had undergone a clinical autopsy including a neuropathological examination. The cortical raspberry density had either been quantified as part of a previous study or was examined de novo in a uniform manner on haematoxylin- and eosin-stained tissue sections from the frontal lobe. The medical records and autopsy reports were assessed regarding neurodegeneration, cerebral infarcts, cerebral atherosclerosis and small vessel disease, cardiac hypertrophy, nephrosclerosis, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. With the patients grouped according to 10-year age interval, non-parametric tests (the Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by pairwise testing with Bonferroni-corrected P values) and multiple linear regression models (not corrected for multiple tests) were performed.
Results: The average raspberry density increased with advancing age. The non-parametric tests demonstrated statistically significant differences in raspberry density when comparing the groups aged 60-99 years and 70-99 years to those aged 20-29 years (P < 0.012) and 30-59 years (P < 0.011), respectively. The multiple linear regression models demonstrated positive associations with age interval (P < 0.001), cerebral atherosclerosis (P = 0.024), cardiac hypertrophy (P = 0.021), hypertension subgrouped for organ damage (P = 0.006), and female sex (P = 0.004), and a tendency towards a negative association with Alzheimer's disease neuropathologic change (P = 0.048).
Conclusion: The raspberry density of the frontal cortex increases with advancing age, but our results also indicate associations with acquired pathologies. Awareness of the biological and pathological context where raspberries occur can guide further research on their origin.
Keywords: Aging; Atherosclerosis; Brain ischemia; Cardiac hypertrophy; Cerebral angiogenesis; Cerebral neovascularization; Cerebrovascular disease; Hypertension; Small vessel disease.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Are cortical microvascular raspberries caused by cerebral hypoperfusion? An exploratory pathological study.Cereb Circ Cogn Behav. 2021 Aug 17;2:100026. doi: 10.1016/j.cccb.2021.100026. eCollection 2021. Cereb Circ Cogn Behav. 2021. PMID: 36324730 Free PMC article.
-
On the regional distribution of cerebral microvascular 'raspberries' and their association with cerebral atherosclerosis and acute circulatory failure.Cereb Circ Cogn Behav. 2023 Jan 7;4:100157. doi: 10.1016/j.cccb.2023.100157. eCollection 2023. Cereb Circ Cogn Behav. 2023. PMID: 36691600 Free PMC article.
-
A cortical microvascular structure in vascular dementia, Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal lobar degeneration and nondemented controls: a sign of angiogenesis due to brain ischaemia?Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2019 Oct;45(6):557-569. doi: 10.1111/nan.12552. Epub 2019 May 9. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30957900 Free PMC article.
-
The pathology of dementia.Br J Psychiatry. 1975;Spec No 9:110-8. Br J Psychiatry. 1975. PMID: 1102009 Review. No abstract available.
-
The pathological basis of multi-infarct dementia.Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1991 Summer;5(2):77-90. doi: 10.1097/00002093-199100520-00005. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1991. PMID: 2059411 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased frontocortical microvascular raspberry density in frontotemporal lobar degeneration compared to Lewy body disease and control cases: a neuropathological study.Free Neuropathol. 2025 Mar 4;6:7. doi: 10.17879/freeneuropathology-2025-6178. eCollection 2025 Jan. Free Neuropathol. 2025. PMID: 40052111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ek Olofsson H, Englund E. A cortical microvascular structure in vascular dementia, Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal lobar degeneration and nondemented controls: a sign of angiogenesis due to brain ischaemia? Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2019;45(6):557–569. doi: 10.1111/nan.12552. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

