Morphology and ASAP analysis of the important zoonotic nematode parasite Baylisascaris procyonis (Stefahski and Zarnowski, 1951), with molecular phylogenetic relationships of Baylisascaris species (Nematoda: Ascaridida)
- PMID: 38087962
- PMCID: PMC10941036
- DOI: 10.1017/S0031182023001312
Morphology and ASAP analysis of the important zoonotic nematode parasite Baylisascaris procyonis (Stefahski and Zarnowski, 1951), with molecular phylogenetic relationships of Baylisascaris species (Nematoda: Ascaridida)
Abstract
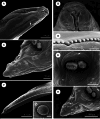
Species of Baylisascaris (Nematoda: Ascarididae) are of great veterinary and zoonotic significance, owing to cause Baylisascariosis or Baylisascariasis in wildlife, captive animals and humans. However, the phylogenetic relationships of the current 10 Baylisascaris species remain unclear. Moreover, our current knowledge of the detailed morphology and morphometrics of the important zoonotic species B. procyonis is still insufficient. The taxonomical status of B. procyonis and B. columnaris remains under debate. In the present study, the detailed morphology of B. procyonis was studied using light and scanning electron microscopy based on newly collected specimens from the raccoon Procyon lotor (Linnaeus) in China. The results of the ASAP analysis and Bayesian inference (BI) using the 28S, ITS, cox1 and cox2 genetic markers did not support that B. procyonis and B. columnaris represent two distinct species. Integrative morphological and molecular assessment challenged the validity of B. procyonis, and suggested that B. procyonis seems to represent a synonym of B. columnaris. Molecular phylogenetic results indicated that the species of Baylisascaris were grouped into 4 clades according to their host specificity. The present study provided new insights into the taxonomic status of B. procyonis and preliminarily clarified the phylogenetic relationships of Baylisascaris species.
Keywords: Ascaridida; Baylisascaris; genetic data; morphology; phylogeny; species delimitation; zoonotic nematode.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Al-Warid HS, Belsare A, Straka K and Gompper ME (2017) Baylisascaris procyonis roundworm infection patterns in raccoons (Procyon lotor) from Missouri and Arkansas, USA. Helminthologia 54, 113–118.
-
- Al-Warid HS, Belsare A, Straka K, Gompper ME and Eggert LS (2018) Genetic polymorphism of Baylisascaris procyonis in host infrapopulations and component populations in the Central USA. Parasitology International 67, 392–396. - PubMed
-
- Barrera MA, Janes JK and Gorrell JC (2022) Molecular phylogenetics and systematics of two enteric helminth parasites (Baylisascaris laevis and Diandrya vancouverensis) in the Vancouver Island marmot (Marmota vancouverensis). International Journal for Parasitology-Parasites and Wildlife 19, 301–310. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bauer C (2013) Baylisascariosis—infections of animals and humans with ‘unusual’ roundworms. Veterinary Parasitology 193, 404–412. - PubMed
-
- Baylis HA and Daubney R (1922) Report on the parasitic nematodes in the collection of the zoological survey of India. Memoirs of the Indian Museum 7, 263–347.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

