Lippia origanoides essential oil possesses anticonvulsant effect in pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures in rats: a behavioral, electroencephalographic, and electromyographic study
- PMID: 38089062
- PMCID: PMC10715423
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1289336
Lippia origanoides essential oil possesses anticonvulsant effect in pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures in rats: a behavioral, electroencephalographic, and electromyographic study
Abstract
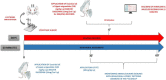
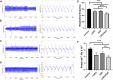
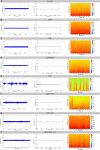
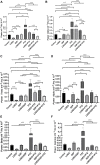
Epilepsy is a neuronal disorder characterized by abnormal excitability of the brain, leading to seizures. Only around 66% of the epileptic patients respond adequately to treatment with existing conventional anticonvulsants, making it necessary to investigate new antiepileptic drugs. The growing research into natural products and their pharmacological properties has become increasingly promising, particularly in the study of essential oils, which are already widely used in popular culture for treating various diseases. The present study evaluated the anticonvulsant effects of Lippia origanoides essential oil (LOEO) (100 mg/kg i. p.) compared to diazepam (DZP) (5 mg/kg i. p.), and the combined administration of these two substances to control convulsions induced by pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) (60 mg/kg i. p.). This evaluation was carried out using 108 male Wistar rats, which were divided into two experiments. Experiment 1-Behavioral assessment: The animals were divided into 4 groups (n = 9): (I) saline solution + PTZ, (II) DZP + PTZ, (III) LOEO + PTZ, (IV) LOEO + DZP + PTZ. The convulsive behavior was induced 30 min after the administration of the tested anticonvulsant drugs, and the observation period lasted 30 min. Experiment 2- Electrocorticographic evaluation: The animals were divided into 8 groups (n = 9): (I) saline solution; (II) LOEO; (III) DZP; (IV) LOEO + DZP; (V) saline + PTZ, (VI) DZP + PTZ (VII) LOEO + PTZ, (VIII) LOEO + DZP + PTZ. PTZ was administered 30 min after LOEO and DZP treatments and electrocorticographic activity was assessed for 15 min. For the control groups, electromyographic recordings were performed in the 10th intercostal space to assess respiratory rate. The results demonstrated that Lippia origanoides essential oil increased the latency time for the appearance of isolated clonic seizures without loss of the postural reflex. The animals had a more intense decrease in respiratory rate when combined with LOEO + DZP. EEG recordings showed a reduction in firing amplitude in the LOEO-treated groups. The combining treatment with diazepam resulted in increased anticonvulsant effects. Therefore, treatment with Lippia origanoides essential oil was effective in controlling seizures, and its combination with diazepam may represent a future option for the treatment of difficult-to-control seizures.
Keywords: Lippia origanoides; electrocorticographic recordings; essential oil; pentylenetetrazol; seizures.
Copyright © 2023 Bastos de Araújo, Gurgel do Amaral, Maia da Fonseca, Rodrigues de Souza, Santos da Paz, Jóia de Mello, Barbosa, Otake Hamoy and Hamoy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aburawi S., Shushni M., Alkateb M. (2021). Effect of Moringa Oleifera extract on the behavior of male albino rats. AlQalam J. Med. Appl. Sci. 4 (2), 1–12. 10.5281/zenodo.4667396 - DOI
-
- de Almeida L. C. N., de Andrade Marques B., Silva R. L., Hamoy A. O., de Mello V. J., Borges R. D. S., et al. (2020). New nanocarried phenobarbital formulation: maintains better control of pentylenetetrazole-Induced seizures. Biotechnol. Rep. (Amst) 9, e00539, e00539. 10.1016/j.btre.2020.e00539 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

