Serum HCoV-spike specific antibodies do not protect against subsequent SARS-CoV-2 infection in children and adolescents
- PMID: 38089581
- PMCID: PMC10711458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108500
Serum HCoV-spike specific antibodies do not protect against subsequent SARS-CoV-2 infection in children and adolescents
Abstract
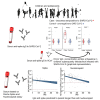
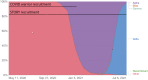
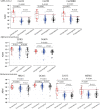
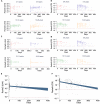
SARS-CoV-2 infections in children are generally asymptomatic or mild and rarely progress to severe disease and hospitalization. Why this is so remains unclear. Here we explore the potential for protection due to pre-existing cross-reactive seasonal coronavirus antibodies and compare the rate of antibody decline for nucleocapsid and spike protein in serum and oral fluid against SARS-CoV-2 within the pediatric population. No differences in seasonal coronaviruses antibody concentrations were found at baseline between cases and controls, suggesting no protective effect from pre-existing immunity against seasonal coronaviruses. Antibodies against seasonal betacoronaviruses were boosted in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. In serum, anti-nucleocapsid antibodies fell below the threshold of positivity more quickly than anti-spike protein antibodies. These findings add to our understanding of protection against infection with SARS-CoV-2 within the pediatric population, which is important when considering pediatric SARS-CoV-2 immunization policies.
Keywords: Health sciences; Immunology; Medical specialty; Medicine; Virology.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
M.D.S. acted on behalf of the University of Oxford as an investigator on studies funded or sponsored by vaccine manufacturers, including AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Novavax, Janssen, Medimmune, and MCM. He received no personal financial payment for this work. Subsequent to this study MDS is employed by Moderna Biotech UK and holds equity in this company. S.N.F. acts on behalf of University Hospital Southampton National Health Service (NHS) Foundation Trust as an investigator or providing consultative advice, or both, on clinical trials and studies of COVID-19 and other vaccines funded or sponsored by vaccine manufacturers including Janssen, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Novavax, Seqirus, Sanofi, Medimmune, Merck, and Valneva. He receives no personal financial payment for this work. M.R. has provided post-marketing surveillance reports on vaccines for Pfizer and GlaxoSmithKline for which a cost recovery charge is made. All other authors declare no competing interests. M.C. and S.L. are funded by US Food and Drug Administration Medical Countermeasures Initiative, contract 75F40120C00085.
Figures

References
-
- Edridge A.W.D., Kaczorowska J., Hoste A.C.R., Bakker M., Klein M., Loens K., Jebbink M.F., Matser A., Kinsella C.M., Rueda P., et al. Seasonal coronavirus protective immunity is short-lasting. Nat. Med. 2020;26:1691–1693. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

