Machine-learning radiomics to predict bone marrow metastasis of neuroblastoma using magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 38090385
- PMCID: PMC10686185
- DOI: 10.1002/cai2.92
Machine-learning radiomics to predict bone marrow metastasis of neuroblastoma using magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
Background: Neuroblastoma is one common pediatric malignancy notorious for high temporal and spatial heterogeneities. More than half of its patients develop distant metastases involving vascularized organs, especially the bone marrow. It is thus necessary to have an economical, noninvasive method without much radiation for follow-ups. Radiomics has been used in many cancers to assist accurate diagnosis but not yet in bone marrow metastasis in neuroblastoma.
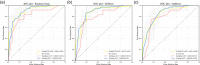
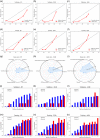
Methods: A total of 182 patients with neuroblastoma were retrospectively collected and randomly divided into the training and validation sets. Five-hundred and seventy-two radiomics features were extracted from magnetic resonance imaging, among which 41 significant ones were selected via T-test for model development. We attempted 13 machine-learning algorithms and eventually chose three best-performed models. The integrative performance evaluations are based on the area under the curves (AUCs), calibration curves, risk deciles plots, and other indexes.
Results: Extreme gradient boosting, random forest (RF), and adaptive boosting were the top three to predict bone marrow metastases in neuroblastoma while RF was the most accurate one. Its AUC was 0.90 (0.86-0.93), F1 score was 0.82, sensitivity was 0.76, and negative predictive value was 0.79 in the training set. The values were 0.82 (0.71-0.93), 0.80, 0.75, and 0.92 in the validation set, respectively.
Conclusions: Radiomics models are likely to contribute more to metastatic diagnoses and the formulation of personalized healthcare strategies in clinics. It has great potential of being a revolutionary method to replace traditional interventions in the future.
Keywords: bone marrow metastasis; machine learning; magnetic resonance imaging; neuroblastoma; radiomics.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Innovation published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Tsinghua University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Professor Xuntao Yin is the member of the Cancer Innovation Editorial Board. To minimize bias, he was excluded from all editorial decision‐making related to the acceptance of this article for publication. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

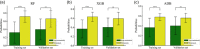
Similar articles
-
Radiomics models to predict bone marrow metastasis of neuroblastoma using CT.Cancer Innov. 2024 Jun 28;3(5):e135. doi: 10.1002/cai2.135. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cancer Innov. 2024. PMID: 38948899 Free PMC article.
-
A machine learning radiomics model based on bpMRI to predict bone metastasis in newly diagnosed prostate cancer patients.Magn Reson Imaging. 2024 Apr;107:15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2023.12.009. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Magn Reson Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38181835
-
Machine learning-based Radiomics analysis for differentiation degree and lymphatic node metastasis of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 Nov 24;21(1):1268. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08947-6. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34819043 Free PMC article.
-
Constructing a Deep Learning Radiomics Model Based on X-ray Images and Clinical Data for Predicting and Distinguishing Acute and Chronic Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures: A Multicenter Study.Acad Radiol. 2024 May;31(5):2011-2026. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2023.10.061. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Acad Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38016821
-
Machine learning models for differential diagnosing HER2-low breast cancer: A radiomics approach.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Aug 16;103(33):e39343. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039343. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39151526 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Risk stratification in neuroblastoma patients through machine learning in the multicenter PRIMAGE cohort.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 21;15:1528836. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1528836. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40061893 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Bone Marrow Metastasis in Neuroblastoma: An Explainable Machine Learning Approach Using Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography Radiomics Features.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241290386. doi: 10.1177/15330338241290386. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39440370 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral therapy can effectively suppress irAEs in HBV positive hepatocellular carcinoma treated with ICIs: validation based on multi machine learning.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 27;15:1516524. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1516524. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39931579 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics models to predict bone marrow metastasis of neuroblastoma using CT.Cancer Innov. 2024 Jun 28;3(5):e135. doi: 10.1002/cai2.135. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cancer Innov. 2024. PMID: 38948899 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-cancer secreted proteome and skeletal muscle regulation: insight from a proteogenomic data-driven knowledge base.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Jan 15;25(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01524-7. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39812750 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
