Application of organoids in otolaryngology: head and neck surgery
- PMID: 38091101
- PMCID: PMC10942880
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-023-08348-4
Application of organoids in otolaryngology: head and neck surgery
Abstract
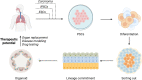
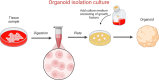
Purpose: The purpose of this review is to systematically summarize the application of organoids in the field of otolaryngology and head and neck surgery. It aims to shed light on the current advancements and future potential of organoid technology in these areas, particularly in addressing challenges like hearing loss, cancer research, and organ regeneration.
Methods: Review of current literature regrading organoids in the field of otolaryngology and head and neck surgery.
Results: The review highlights several advancements in the field. In otology, the development of organoid replacement therapies offers new avenues for treating hearing loss. In nasal science, the creation of specific organoid models aids in studying nasopharyngeal carcinoma and respiratory viruses. In head and neck surgery, innovative approaches for squamous cell carcinoma prediction and thyroid regeneration using organoids have been developed.
Conclusion: Organoid research in otolaryngology-head and neck surgery is still at an early stage. This review underscores the potential of this technology in advancing our understanding and treatment of various conditions, predicting a transformative impact on future medical practices in these fields.
Keywords: 3D tissue model; Organoids; Otolaryngology—head and neck surgery; Stem cells; Tumor prediction model.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD AND NECK SURGERY - VARIETY OF PATHOLOGIES AND MANAGEMENT OPTIONS].Harefuah. 2020 Feb;159(1):74-76. Harefuah. 2020. PMID: 32048483 Hebrew.
-
Clinical applications of three-dimensional printing in otolaryngology-head and neck surgery: A systematic review.Laryngoscope. 2019 Sep;129(9):2045-2052. doi: 10.1002/lary.27831. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Laryngoscope. 2019. PMID: 30698840
-
The current status of nanotechnological approaches to therapy and drug delivery in otolaryngology: A contemporary review.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022 Oct 20;7(6):1762-1772. doi: 10.1002/lio2.952. eCollection 2022 Dec. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 36544970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D Printing in Otolaryngology Surgery: Descriptive Review of Literature to Define the State of the Art.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Dec 29;11(1):108. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11010108. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36611568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D Bioprinting in Otolaryngology: A Review.Adv Healthc Mater. 2023 Jul;12(19):e2203268. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202203268. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023. PMID: 36921327 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inner Ear Organoid as a Preclinical Model of Hearing Regeneration: Progress and Applications.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2025 Jul 25. doi: 10.1007/s12015-025-10941-5. Online ahead of print. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2025. PMID: 40711673 Review.
References
-
- Kretzschmar K, Clevers H. Organoids: modeling development and the stem cell niche in a dish. Dev Cell. 2016;38(6):590–600. - PubMed
-
- Drost J, Clevers H. Organoids in cancer research. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18(7):407–418. - PubMed
-
- Rossi G, Manfrin A, Lutolf MP. Progress and potential in organoid research. Nat Rev Genet. 2018;19(11):671–687. - PubMed
-
- Ray K. Next-generation intestinal organoids. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;17(11):649. - PubMed
-
- Ray K. Development: modelling human stomach development with gastric organoids. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14(2):68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources