Cysteine desulfurase (IscS)-mediated fine-tuning of bioenergetics and SUF expression prevents Mycobacterium tuberculosis hypervirulence
- PMID: 38091389
- PMCID: PMC10848736
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adh2858
Cysteine desulfurase (IscS)-mediated fine-tuning of bioenergetics and SUF expression prevents Mycobacterium tuberculosis hypervirulence
Abstract
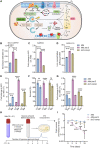
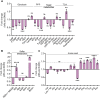
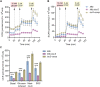
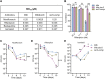
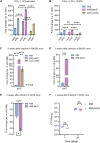
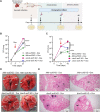
Iron-sulfur (Fe-S) biogenesis requires multiprotein assembly systems, SUF and ISC, in most prokaryotes. M. tuberculosis (Mtb) encodes a complete SUF system, the depletion of which was bactericidal. The ISC operon is truncated to a single gene iscS (cysteine desulfurase), whose function remains uncertain. Here, we show that MtbΔiscS is bioenergetically deficient and hypersensitive to oxidative stress, antibiotics, and hypoxia. MtbΔiscS resisted killing by nitric oxide (NO). RNA sequencing indicates that IscS is important for expressing regulons of DosR and Fe-S-containing transcription factors, WhiB3 and SufR. Unlike wild-type Mtb, MtbΔiscS could not enter a stable persistent state, continued replicating in mice, and showed hypervirulence. The suf operon was overexpressed in MtbΔiscS during infection in a NO-dependent manner. Suppressing suf expression in MtbΔiscS either by CRISPR interference or upon infection in inducible NO-deficient mice arrests hypervirulence. Together, Mtb redesigned the ISC system to "fine-tune" the expression of SUF machinery for establishing persistence without causing detrimental disease in the host.
Figures



References
-
- F. C. Fang, Antimicrobial reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: Concepts and controversies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2, 820–832 (2004). - PubMed
-
- I. Elchennawi, S. Ollagnier de Choudens, Iron–Sulfur Clusters toward Stresses: Implication for Understanding and Fighting Tuberculosis. Inorganics 10, 174 (2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

