The immunobiology of herpes simplex virus encephalitis and post-viral autoimmunity
- PMID: 38092513
- PMCID: PMC10994539
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awad419
The immunobiology of herpes simplex virus encephalitis and post-viral autoimmunity
Abstract
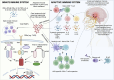
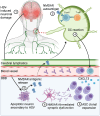
Herpes simplex virus encephalitis (HSE) is the leading cause of non-epidemic encephalitis in the developed world and, despite antiviral therapy, mortality and morbidity is high. The emergence of post-HSE autoimmune encephalitis reveals a new immunological paradigm in autoantibody-mediated disease. A reductionist evaluation of the immunobiological mechanisms in HSE is crucial to dissect the origins of post-viral autoimmunity and supply rational approaches to the selection of immunotherapeutics. Herein, we review the latest evidence behind the phenotypic progression and underlying immunobiology of HSE including the cytokine/chemokine environment, the role of pathogen-recognition receptors, T- and B-cell immunity and relevant inborn errors of immunity. Second, we provide a contemporary review of published patients with post-HSE autoimmune encephalitis from a combined cohort of 110 patients. Third, we integrate novel mechanisms of autoimmunization in deep cervical lymph nodes to explore hypotheses around post-HSE autoimmune encephalitis and challenge these against mechanisms of molecular mimicry and others. Finally, we explore translational concepts where neuroglial surface autoantibodies have been observed with other neuroinfectious diseases and those that generate brain damage including traumatic brain injury, ischaemic stroke and neurodegenerative disease. Overall, the clinical and immunological landscape of HSE is an important and evolving field, from which precision immunotherapeutics could soon emerge.
Keywords: autoimmune encephalitis; herpes simplex virus encephalitis; immunology; immunotherapeutics; viral encephalitis.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
P.K. has served on an advisory board for immune conditions for UCB, Astra Zeneca, Medimmunebio, Infinitopes and Biomunex. S.R.I. has received honoraria and/or research support from UCB, Immunovant, MedImmun, Roche, Cerebral therapeutics, CSL Behring, ONO Pharma and ADC therapeutics. S.R.I. is a co-applicant and receive royalties on patent application WO/2010/046716 entitled ‘Neurological Autoimmune Disorders’. The patent has been licensed for the development of assays for LGI1 and other VGKC-complex antibodies, and coinventors on ‘A Diagnostic Strategy to improve specificity of CASPR2 antibody detection’ reference JA94536P. M.L. receives/has received consultation fees from CSL Behring, Novartis, Roche and Octapharma; received travel grants from Merck Serono; and received unrestricted educational grants to organize meetings by Novartis, Biogen Idec, Merck Serono and Bayer.
Figures

References
-
- Boucher A, Herrmann JL, Morand P, et al. Epidemiology of infectious encephalitis causes in 2016. Med Mal Infect. 2017;47:221–235. - PubMed
-
- Hjalmarsson A, Blomqvist P, Sköldenberg B. Herpes simplex encephalitis in Sweden, 1990–2001: Incidence, morbidity, and mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:875–880. - PubMed
-
- Venkatesan A, Michael BD, Probasco JC, Geocadin RG, Solomon T. Acute encephalitis in immunocompetent adults. Lancet. 2019;393:702–716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

