Lung dendritic-cell metabolism underlies susceptibility to viral infection in diabetes
- PMID: 38093014
- PMCID: PMC10733144
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06803-0
Lung dendritic-cell metabolism underlies susceptibility to viral infection in diabetes
Abstract
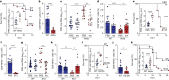
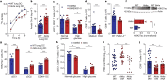
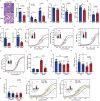
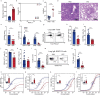
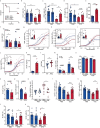
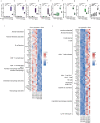
People with diabetes feature a life-risking susceptibility to respiratory viral infection, including influenza and SARS-CoV-2 (ref. 1), whose mechanism remains unknown. In acquired and genetic mouse models of diabetes, induced with an acute pulmonary viral infection, we demonstrate that hyperglycaemia leads to impaired costimulatory molecule expression, antigen transport and T cell priming in distinct lung dendritic cell (DC) subsets, driving a defective antiviral adaptive immune response, delayed viral clearance and enhanced mortality. Mechanistically, hyperglycaemia induces an altered metabolic DC circuitry characterized by increased glucose-to-acetyl-CoA shunting and downstream histone acetylation, leading to global chromatin alterations. These, in turn, drive impaired expression of key DC effectors including central antigen presentation-related genes. Either glucose-lowering treatment or pharmacological modulation of histone acetylation rescues DC function and antiviral immunity. Collectively, we highlight a hyperglycaemia-driven metabolic-immune axis orchestrating DC dysfunction during pulmonary viral infection and identify metabolic checkpoints that may be therapeutically exploited in mitigating exacerbated disease in infected diabetics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
E.E. is a scienrtific cofounder of DayTwo and BiomX and an advisor to Purposebio, Igen, Aposense and Zoe in topics unrelated to this work. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
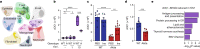
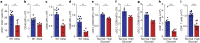
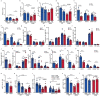
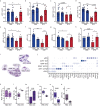
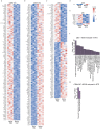

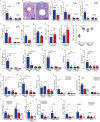
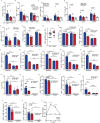

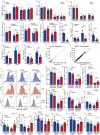
Comment in
-
A case of too much sugar: Lung DCs flummoxed by flu.Immunity. 2024 Feb 13;57(2):203-205. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.01.014. Immunity. 2024. PMID: 38354700
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

