Therapeutic potential for renal fibrosis by targeting Smad3-dependent noncoding RNAs
- PMID: 38093516
- PMCID: PMC10861968
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.12.009
Therapeutic potential for renal fibrosis by targeting Smad3-dependent noncoding RNAs
Abstract
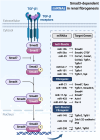
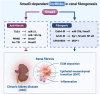
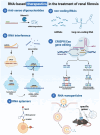
Renal fibrosis is a characteristic hallmark of chronic kidney disease (CKD) that ultimately results in renal failure, leaving patients with few therapeutic options. TGF-β is a master regulator of renal fibrosis and mediates progressive renal fibrosis via both canonical and noncanonical signaling pathways. In the canonical Smad signaling, Smad3 is a key mediator in tissue fibrosis and mediates renal fibrosis via a number of noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs). In this regard, targeting Smad3-dependent ncRNAs may offer a specific therapy for renal fibrosis. This review highlights the significance and innovation of TGF-β/Smad3-associated ncRNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in renal fibrogenesis. In addition, the underlying mechanisms of these ncRNAs and their future perspectives in the treatment of renal fibrosis are discussed.
Keywords: Smad3; TGF-β; noncoding RNAs; renal fibrosis; therapy.
Copyright © 2023 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Central role of dysregulation of TGF-β/Smad in CKD progression and potential targets of its treatment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 May;101:670-681. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.090. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29518614 Review.
-
TGF-β Mediates Renal Fibrosis via the Smad3-Erbb4-IR Long Noncoding RNA Axis.Mol Ther. 2018 Jan 3;26(1):148-161. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.09.024. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Mol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29102563 Free PMC article.
-
Smad3 Signatures in Renal Inflammation and Fibrosis.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Mar 28;18(7):2795-2806. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.71595. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35541902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long noncoding RNA lnc-TSI inhibits renal fibrogenesis by negatively regulating the TGF-β/Smad3 pathway.Sci Transl Med. 2018 Oct 10;10(462):eaat2039. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aat2039. Sci Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30305452
-
Transforming growth factor-β signalling in renal fibrosis: from Smads to non-coding RNAs.J Physiol. 2018 Aug;596(16):3493-3503. doi: 10.1113/JP274492. Epub 2018 Jun 28. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29781524 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Review of Chinese medicine intervention in PI3K/AKT pathway to regulate fibrosis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jul 11;104(28):e42957. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042957. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40660593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary addition of magnesium hydride nanoparticles: a breakthrough in combating high-fat diet-induced chronic kidney disease.Med Gas Res. 2025 Sep 1;15(3):374-382. doi: 10.4103/mgr.MEDGASRES-D-24-00090. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Med Gas Res. 2025. PMID: 40251018 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in therapeutic use of transforming growth factor-beta inhibitors in cancer and fibrosis.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 25;15:1489701. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1489701. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40352593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation of potential targets and pathways in chronic kidney disease associated with renal fibrosis.J Transl Med. 2025 Apr 2;23(1):387. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-06058-x. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40176090 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of herbal monomers on ferroptosis in renal fibrosis: a review and mechanistic study.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 22;16:1610573. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1610573. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40766752 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lv J.C., Zhang L.X. Prevalence and Disease Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019;1165:3–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

