Glucagon-like peptide agonists: A prospective review
- PMID: 38093651
- PMCID: PMC10782143
- DOI: 10.1002/edm2.462
Glucagon-like peptide agonists: A prospective review
Abstract
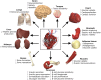
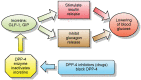
Background: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have emerged as promising therapeutic options for addressing Type-2 diabetes, obesity, and related conditions. Among these, semaglutide, tirzepatide, liraglutide etc., all notable GLP-1RA, have gained attention owing to their favourable pharmacological properties and clinical efficacy.
Aims: This comprehensive review aims to provide a detailed analysis of both the currently available GLP-1RAs in the market and those undergoing clinical trials. The focus is on examining their mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, efficacy in glycemic control and weight management, safety profile, and potential applications.
Materials & methods: The review employs a systematic approach to gather information on GLP-1RAs. Relevant literature from the currently literature and ongoing clinical trials is thoroughly examined. Detailed scrutiny is applied to understand the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetic properties, and clinical outcomes of these agents.
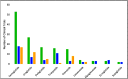
Results: The review presents a comprehensive overview of the GLP-1RAs, highlighting their distinct mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetic profiles, and clinical effectiveness in glycemic control and weight management. Safety profiles are also discussed, providing a holistic understanding of these therapeutic agents.
Discussion: The findings are discussed in the context of advancements in the field of GLP-1RAs. Potential applications beyond diabetes and obesity are explored, shedding light on the broader implications of these agents in managing related conditions.
Conclusion: In conclusion, this review underscores the significance of GLP-1RAs, with a specific focus on semaglutide, in the management of type 2 diabetes, obesity, and beyond. By synthesizing information on their mechanisms, pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and safety, this review provides valuable insights into the potential benefits these agents offer, contributing to the ongoing discourse in the field.
Keywords: GLP-1; GLP-2; cancer; diabetes; glucagon; hormones; neurological disorders.
© 2023 The Authors. Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Pharmaceutical Scientist, Inc. is a professional consulting company in pharmaceutical sciences.
Figures

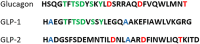
Similar articles
-
Real-world evidence on the utilization, clinical and comparative effectiveness, and adverse effects of newer GLP-1RA-based weight-loss therapies.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Apr;27 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):66-88. doi: 10.1111/dom.16364. Epub 2025 Apr 8. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 40196933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular safety and benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017 Mar;16(3):351-363. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2017.1281246. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017. PMID: 28102093
-
Long-acting GLP-1RAs: An overview of efficacy, safety, and their role in type 2 diabetes management.JAAPA. 2020 Aug;33(S8 Suppl 1):3-18. doi: 10.1097/01.JAA.0000669456.13763.bd. JAAPA. 2020. PMID: 32756220 Review.
-
Weight Loss and Maintenance Related to the Mechanism of Action of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists.Adv Ther. 2021 Jun;38(6):2821-2839. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01710-0. Epub 2021 May 11. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 33977495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment Strategy for Type 2 Diabetes with Obesity: Focus on Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists.Clin Ther. 2017 Jun;39(6):1244-1264. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.03.013. Epub 2017 May 16. Clin Ther. 2017. PMID: 28526416 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Therapeutics for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-A Look at the Past Decade and a Glimpse into the Future.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 21;12(7):1386. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071386. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39061960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemerin in Participants with or without Insulin Resistance and Diabetes.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 22;12(4):924. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040924. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672278 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Therapy Evolution from Defining a Sub-population to Crossing Multi-indications.Adv Pharm Bull. 2024 Dec 30;14(4):737-744. doi: 10.34172/apb.43306. Epub 2024 Sep 15. Adv Pharm Bull. 2024. PMID: 40190666 Free PMC article.
-
Cluster Analysis in Diabetes Research: A Systematic Review Enhanced by a Cross-Sectional Study.J Clin Med. 2025 May 21;14(10):3588. doi: 10.3390/jcm14103588. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40429583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Up-to-date Treatment for Diabetes and Prevention of its Complications.Juntendo Iji Zasshi. 2024 Dec 31;70(6):400-407. doi: 10.14789/ejmj.JMJ24-0030-R. eCollection 2024. Juntendo Iji Zasshi. 2024. PMID: 39840001 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campbell RK, White JR Jr. Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2008;48 Suppl 1:S40‐S45. - PubMed
-
- GCG glucagon [Homo sapiens (human)] – Gene – NCBI. (n.d.). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/2641
-
- Stryer L. Biochemistry. 4th ed. WH Freeman and Company; 1995.
-
- MacDonald MJ. Synergistic potent insulin release by combinations of weak secretagogues in pancreatic islets and INS‐1 cells. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(9):6043‐6052. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

