The Telltale Botox: Botulinum Toxin Injection by an Expert Hand as an Intracranial Aneurysm Detector
- PMID: 38093722
- PMCID: PMC10718318
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005452
The Telltale Botox: Botulinum Toxin Injection by an Expert Hand as an Intracranial Aneurysm Detector
Abstract
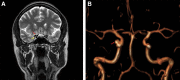
Complications in aesthetic medicine can be considered a consequence of the inexperience of the performing physician, but in some cases, they can unveil far more serious conditions, hitherto silent. We present a case of a 48-year-old patient who, following botulinum toxin type A (Botox) injection for treatment of forehead wrinkles, returned to our attention 12 days later for a discrete, newly onset right eyelid ptosis. This ptosis was a telltale sign of the presence of an intracranial aneurysm closely related with the oculomotor nerve. The lack of compensatory action by the frontalis muscle in maintaining the eyelid in position allowed us to highlight the extrinsic compression deficit of the oculomotor nerve. Subsequently, the patient underwent endovascular treatment of the aneurysm, leading to complete resolution of the case.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Ahsanuddin S, Roy S, Nasser W, et al. . Adverse events associated with botox as reported in a food and drug administration database. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021;45:1201–1209. - PubMed
-
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons. 2018 Plastic surgery statistics: ASPS national clearinghouse of plastic surgery procedural statistics. Available at https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2018/plastic-su.... Published 2018. Accessed November 10, 2023.
-
- Lagueny A, Burbaud P. Mécanisme d’action, indication et résultats des traitements par la toxine botulinique [Mechanism of action, clinical indication and results of treatment of botulinum toxin]. Neurophysiol Clin. 1996. French;26:216–226. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
