A bibliometric analysis of PCSK9 inhibitors from 2007 to 2022
- PMID: 38093957
- PMCID: PMC10716461
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1218968
A bibliometric analysis of PCSK9 inhibitors from 2007 to 2022
Abstract
Background: Since the approval of the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) monoclonal antibodies for marketing in 2015, PCSK9 inhibitors have attracted significant interest in the field of cardiovascular endocrinology. A large number of clinical trials have confirmed the efficacy and safety of PCSK9 inhibitors in reducing cholesterol and the risk of cardiovascular events. No bibliometric analysis of PCSK9 inhibitors has been performed as of yet. This study aims to analyze the research trends and hotspots of PCSK9 inhibitors through bibliometric analysis.
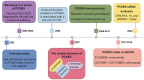
Methods: We searched the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database for PCSK9 inhibitor-related publications from 2007 to 2022. Data visualization analysis was performed using CiteSpace software. Microsoft Excel and Graphpad software were used for the drawing of some tables and figures.
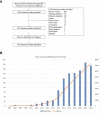
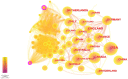
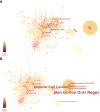
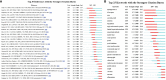
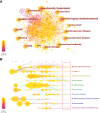
Results: A total of 1072 pieces of literature were retrieved between 2007 and 2022. The number of publications concerning PCSK9 inhibitors is growing annually. The top five countries with the most articles published were the United States, England, Canada, Italy, and France. Harvard University, Amgen, Brigham & Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, and Imperial College London are the five institutions with the highest output. The Journal of Clinical Lipidology is the most popular journal in this field. The most frequently cited journal is the New England Journal of Medicine. As for authors, Sabatine MS and Giugliano RP from Brigham & Women's Hospital have the highest number of published articles. Amgen is the funding agency for most of the research. According to keyword analysis, "low density lipoprotein", "familial hypercholesterolemia", "PCSK9 inhibitor", "PCSK9", and "efficacy" are the five keywords with the highest frequency of co-occurrence.
Conclusion: The past 15 years have witnessed a rapid and fruitful development of PCSK9 inhibitors. The research trend and focus for PCSK9 inhibitors are from the mechanism of reducing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol to related clinical trials. Developed countries such as the United States have contributed prominently in this area. Coronary artery and inflammation are currently at the forefront of research in the field and are in an explosion period.
Keywords: PCSK9 inhibitors; bibliometric analysis; cardiovascular endocrinology; data visualization; hotspots; trend.
Copyright © 2023 Luo, Tang, Wu, Chen, Fang and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Advancing Research on Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Inhibitors: A Scientometric Analysis.Malays J Med Sci. 2024 Aug;31(4):14-34. doi: 10.21315/mjms2024.31.4.2. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Malays J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39247108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring research trends and hotspots on PCSK9 inhibitor studies: a bibliometric and visual analysis spanning 2007 to 2023.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Nov 22;11:1474472. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1474472. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39650150 Free PMC article.
-
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors: Present perspectives and future horizons.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2016 Oct;26(10):853-62. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2016.05.006. Epub 2016 May 30. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2016. PMID: 27352986 Review.
-
Global trends and research hotspots of PCSK9 and cardiovascular disease: a bibliometric and visual analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jun 3;11:1336264. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1336264. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38887452 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting PCSK9 as a promising new mechanism for lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Aug;164:183-94. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.04.011. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27133571 Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: New and emerging lipid-lowering therapies for reducing cardiovascular risk: beyond statins.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jan 15;11:1364170. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1364170. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38287985 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Advances in Oral Biomacromolecule Therapies for Metabolic Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 12;17(2):238. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020238. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40006605 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Seidah NG, Benjannet S, Wickham L, Marcinkiewicz J, Jasmin SB, Stifani S, et al. . The secretory proprotein convertase neural apoptosis-regulated convertase1 (NARC-1): Liver regeneration and neuronal differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2003) 100:928–33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0335507100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

