Autonomic Modulation of Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 38094692
- PMCID: PMC10714180
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2023.03.019
Autonomic Modulation of Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
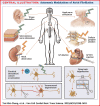
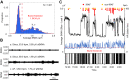
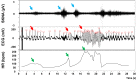
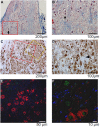
The autonomic nervous system plays a vital role in cardiac arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation (AF). Therefore, reducing the sympathetic tone via neuromodulation methods may be helpful in AF control. Myocardial ischemia is associated with increased sympathetic tone and incidence of AF. It is an excellent disease model to understand the neural mechanisms of AF and the effects of neuromodulation. This review summarizes the relationship between autonomic nervous system and AF and reviews methods and mechanisms of neuromodulation. This review proposes that noninvasive or minimally invasive neuromodulation methods will be most useful in the future management of AF.
Keywords: neuECG; neuroremodeling; skin sympathetic nerve activity; stellate ganglion; sympathetic nerve activity.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was supported in part by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (grant MOST 110-2314-B-037-111), the Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital Research Foundation (grants SI11001, SI11101, KMUH105-5M07, KMUH-S10707, and NK111P24), the US National Institutes of Health (grants R01HL139829 and OT2OD028190), and the Burns and Allen Chair in Cardiology Research, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California. Dr Peng-Sheng Chen and Lan S. Chen are co-inventors of U.S. Patents awarded to Indiana University. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Shen M.J., Zipes D.P. Role of the autonomic nervous system in modulating cardiac arrhythmias. Circ Res. 2014;114(6):1004–1021. - PubMed
-
- Tan A.Y., Li H., Wachsmann-Hogiu S., Chen L.S., Chen P.S., Fishbein M.C. Autonomic innervation and segmental muscular disconnections at the human pulmonary vein-atrial junction: implications for catheter ablation of atrial-pulmonary vein junction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48(1):132–143. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

