A Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Case Study to Promote Interprofessional Learning (IPL) Between Audiology and Biomedical Science Students in Higher Education
- PMID: 38094711
- PMCID: PMC10716233
- DOI: 10.3389/bjbs.2023.11680
A Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Case Study to Promote Interprofessional Learning (IPL) Between Audiology and Biomedical Science Students in Higher Education
Abstract
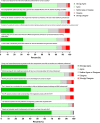
Modern and effective patient care requires specialist healthcare professionals working together. Interprofessional learning (IPL) seeks to provide opportunities for different healthcare disciplines to learn with, from and about each other. This study focused on the delivery and evaluation of a cytomegalovirus (CMV) case study workshop to facilitate IPL between two Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC) regulated courses: Biomedical Science and Audiology. The 2 h online workshop consisted of 1) defining the roles, responsibilities and skills of the two healthcare professions, 2) the structure of the Biomedical Science and Audiology departments, 3) routes to HCPC registration, 4) core curriculum of both degree programmes and 5) interpreting interdisciplinary data related to a CMV patient case. The workshop was interactive, with the virtual learning environment promoting peer discussions and the use of online polling. Student responses were collected through an online questionnaire. A total of 108 respondents completed a post-event survey and Mann-Whitney U tests revealed there were no significant differences in the responses between the two student cohorts in response to each of the survey statements (p > 0.05). A total of 82.4% of students agreed that they need to know the role of other healthcare professionals for their future practice, whilst 84.2% agreed that the CMV case study was a good format to facilitate effective IPL. A total of 93.5% of respondents recognised the importance of both professions in diagnosing a patient with CMV. Thematic analysis identified four common themes, including appreciation of shared roles, recognition of similarities in registration pathways, working together to provide holistic patient care and the role of clinicians in the patient journey. This novel collaboration between Biomedical Science and Audiology facilitated effective IPL whilst meeting the interprofessional education HCPC requirements. Collaborative working is an essential component of delivering effective patient care and allied healthcare degrees need to provide opportunities within their curriculum to foster this. We hope this study encourages other higher education institutes to expand and develop their current IPL activities to include a broader spectrum of healthcare courses.
Keywords: audiology; biomedical science; higher education; interprofessional learning; patient care.
Copyright © 2023 Bashir, Pallett, Rana and Hussain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Virtual Approach to Promote Inter-Professional Learning (IPL) Between Biomedical Science and Medicine in Higher Education for the Benefit of Patient Care.Front Public Health. 2021 Oct 6;9:747751. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.747751. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34692629 Free PMC article.
-
Using complexity theory to develop a student-directed interprofessional learning activity for 1220 healthcare students.BMC Med Educ. 2016 Aug 8;16:199. doi: 10.1186/s12909-016-0717-y. BMC Med Educ. 2016. PMID: 27502773 Free PMC article.
-
Is Interprofessional Learning Only Meant for Professions Within Healthcare? - A Qualitative Analysis of Associations with the Term Interprofessional Collaborative Learning Among Professional Students.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2022 Sep 2;15:1945-1954. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S376074. eCollection 2022. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2022. PMID: 36081580 Free PMC article.
-
Interprofessional learning and rural paramedic care.Rural Remote Health. 2014;14(3):2821. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Rural Remote Health. 2014. PMID: 25036770 Review.
-
Content validation of an interprofessional learning video peer assessment tool.BMC Med Educ. 2017 Dec 16;17(1):258. doi: 10.1186/s12909-017-1099-5. BMC Med Educ. 2017. PMID: 29246261 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gantayet-Mathur A, Chan K, Kalluri M. Patient-Centered Care and Interprofessional Collaboration in Medical Resident Education: Where We Stand and Where We Need to Go. Humanities Soc Sci Commun (2022) 9(1):206–24. 10.1057/s41599-022-01221-5 - DOI
-
- Health and Care Professions Council. Standards of Education and Training (2017). Available From: https://www.hcpc-uk.org/resources/standards/standards-of-education-and-t... (Accessed July 26, 2021).

