TCM and related active compounds in the treatment of gout: the regulation of signaling pathway and urate transporter
- PMID: 38094893
- PMCID: PMC10716793
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1275974
TCM and related active compounds in the treatment of gout: the regulation of signaling pathway and urate transporter
Abstract
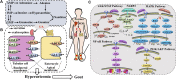
Gout represents a metabolic ailment resulting from the accumulation of monosodium urate crystals within joints, causing both inflammation and, harm to tissues. The primary contributor to gout's emergence is an elevated presence of serum urate, which is under the regulation of kidney and, gut urate transporters. Mitigating this risk factor is crucial for averting gout's onset. Several treatments rooted in TCM and related active compounds have demonstrated efficacy in managing gout, skillfully regulating serum uric acid (UA) levels and curbing inflammation's progression. This analysis compiles key foundational research concerning the molecular signaling pathways and UA transporters linked to gout, under the regulation of TCM. The focus includes individual botanical drug, active compounds, and TCM formulations, which have been consolidated and examined in this overview. The primary keywords chosen were "gout, hyperuricemia, gouty arthritis, traditional Chinese medicine, Chinese botanical drug, medicinal botanical drug, and natural plant". Various relevant literature published within the last 5 years were gathered from electronic databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, CNKI, and others. The findings revealed that TCM has the capacity to modulate various signaling pathways, including MAPK, NF-κB, PI3K/Akt, NLRP3 and JAK/STAT. Additionally, it impacts UA transporters like URAT1, GLUT9, ABCG2, as well as OATs and OCTs, thereby contributing to gout treatment. TCM helps maintain a balanced inflammatory interaction and facilitates UA excretion. This study enhances our understanding of TCM's anti-gout mechanisms and introduces novel perspectives for establishing the clinical significance and future prospects of TCM-based gout treatment.
Keywords: TCM; gout; review; signaling pathway; urate transporter.
Copyright © 2023 Sun, Yang, Sun, Sun, Wei, Han, Wang, Kong and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytochemicals in traditional Chinese medicine can treat gout by regulating intestinal flora through inactivating NLRP3 and inhibiting XOD activity.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;74(7):919-929. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgac024. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35640306
-
Paeonia × suffruticosa Andrews leaf extract and its main component apigenin 7-O-glucoside ameliorate hyperuricemia by inhibiting xanthine oxidase activity and regulating renal urate transporters.Phytomedicine. 2023 Sep;118:154957. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154957. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37478683
-
Dendrobium officinalis six nostrum ameliorates urate under-excretion and protects renal dysfunction in lipid emulsion-induced hyperuricemic rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Dec;132:110765. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110765. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 33120237
-
Gout: epitome of painful arthritis.Metabolism. 2010 Oct;59 Suppl 1:S32-6. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2010.07.009. Metabolism. 2010. PMID: 20837191 Review.
-
Recent approaches to gout drug discovery: an update.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2020 Aug;15(8):943-954. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2020.1755251. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2020. PMID: 32329387 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Therapeutic Targets for Hyperuricemia: Systematic Genome-Wide Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization Analysis.Biomedicines. 2025 Apr 23;13(5):1022. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051022. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40426853 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating Lipid Metabolism in Gout: A New Perspective with Therapeutic Potential.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Nov 12;17:5203-5217. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S499413. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39554874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the mechanisms of resveratrol in the treatment of gouty arthritis through the integration of network pharmacology and metabolics.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 29;15:1438405. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1438405. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39534253 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Rg5 modulates the TLR4 and BCL-2 pathways by inhibiting NOX1, thereby alleviating inflammation, apoptosis and pyroptosis in hyperuricemia nephropathy.J Ginseng Res. 2025 Jul;49(4):426-437. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2025.03.009. Epub 2025 Mar 25. J Ginseng Res. 2025. PMID: 40621077 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic and Cellular Mechanisms of Drug-Induced Ototoxicity and Nephrotoxicity: Therapeutic Implications of Uric Acid Modulation.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Apr;12(16):e2415041. doi: 10.1002/advs.202415041. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40041973 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources