An observational, multicenter, registry-based cohort study of Turkish Neonatal Society in neonates with Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
- PMID: 38096201
- PMCID: PMC10721008
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295759
An observational, multicenter, registry-based cohort study of Turkish Neonatal Society in neonates with Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
Abstract
Background: Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a significant cause of mortality and short- and long-term morbidities. Therapeutic hypothermia (TH) has been shown to be the standard care for HIE of infants ≥36 weeks gestational age (GA), as it has been demonstrated to reduce the rates of mortality, and adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes. This study aims to determine the incidence of HIE in our country, to assess the TH management in infants with HIE, and present short-term outcomes of these infants.
Methods: The Turkish Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy Online Registry database was established for this multicenter, prospective, observational, nationally-based cohort study to evaluate the data of infants born at ≥34 weeks GA who displayed evidence of neonatal encephalopathy (NE) between March, 2020 and April 2022.
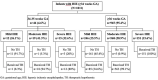
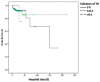
Results: The incidence of HIE among infants born at ≥36 weeks GA (n = 965) was 2.13 per 1000 live births (517:242440), and accounting for 1.55% (965:62062) of all neonatal intensive care unit admissions. The rates of mild, moderate and severe HİE were 25.5% (n = 246), 58.9% (n = 568), and 15.6% (n = 151), respectively. Infants with severe HIE had higher rates of abnormal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings, and mortality (p<0.001). No significant difference in mortality and abnormal MRI results was found according to the time of TH initiation (<3 h, 3-6 h and >6 h) (p>0.05). TH was administered to 85 (34.5%) infants with mild HIE, and of those born of 34-35 weeks of GA, 67.4% (n = 31) received TH. A total of 58 (6%) deaths were reported with a higher mortality rate in infants born at 34-35 weeks of GA (OR 3.941, 95% Cl 1.446-10.7422, p = 0.007).
Conclusion: The incidence of HIE remained similar over time with a reduction in mortality rate. The timing of TH initiation, whether <3 or 3-6 h, did not result in lower occurrences of brain lesions on MRI or mortality. An increasing number of infants with mild HIE and late preterm infants with HIE are receiving TH; however, the indications for TH require further clarification. Longer follow-up studies are necessary for this vulnerable population.
Copyright: © 2023 Okulu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Executive summary: Neonatal encephalopathy and neurologic outcome, second edition. Report of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Task Force on Neonatal Encephalopathy. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123(4).896–901. - PubMed
-
- Battin M, Sadler L, Masson V, Farquhar C, Neonatal Encephalopathy Working Group of the PMMRC. Neonatal encephalopathy in New Zealand: Demographics and clinical outcome. J Paediatr Child Health. 2016;52(6):632–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous