Single-cell RNA-seq and single-cell bisulfite-sequencing reveal insights into yak preimplantation embryogenesis
- PMID: 38097189
- PMCID: PMC10821408
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105562
Single-cell RNA-seq and single-cell bisulfite-sequencing reveal insights into yak preimplantation embryogenesis
Abstract
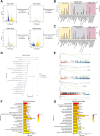
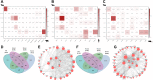
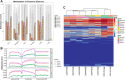
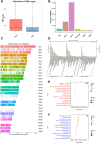
Extensive epigenetic reprogramming occurs during preimplantation embryonic development. However, the impact of DNA methylation in plateau yak preimplantation embryos and how epigenetic reprogramming contributes to transcriptional regulatory networks are unclear. In this study, we quantified gene expression and DNA methylation in oocytes and a series of yak embryos at different developmental stages and at single-cell resolution using single-cell bisulfite-sequencing and RNA-seq. We characterized embryonic genome activation and maternal transcript degradation and mapped epigenetic reprogramming events critical for embryonic development. Through cross-species transcriptome analysis, we identified 31 conserved maternal hub genes and 39 conserved zygotic hub genes, including SIN3A, PRC1, HDAC1/2, and HSPD1. Notably, by combining single-cell DNA methylation and transcriptome analysis, we identified 43 candidate methylation driver genes, such as AURKA, NUSAP1, CENPF, and PLK1, that may be associated with embryonic development. Finally, using functional approaches, we further determined that the epigenetic modifications associated with the histone deacetylases HDAC1/2 are essential for embryonic development and that the deubiquitinating enzyme USP7 may affect embryonic development by regulating DNA methylation. Our data represent an extensive resource on the transcriptional dynamics of yak embryonic development and DNA methylation remodeling, and provide new insights into strategies for the conservation of germplasm resources, as well as a better understanding of mammalian early embryonic development that can be applied to investigate the causes of early developmental disorders.
Keywords: embryo development; embryonic genome activation; single-cell RNA-seq; whole-genome bisulfite sequencing; yak.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Essential roles of HDAC1 and 2 in lineage development and genome-wide DNA methylation during mouse preimplantation development.Epigenetics. 2020 Apr;15(4):369-385. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2019.1669375. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Epigenetics. 2020. PMID: 31533525 Free PMC article.
-
Male fertility status is associated with DNA methylation signatures in sperm and transcriptomic profiles of bovine preimplantation embryos.BMC Genomics. 2017 Apr 5;18(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3673-y. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28381255 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome transcriptome and DNA methylome analyses reveal molecular abnormalities during the oocyte-to-embryo transition in preimplantation embryos derived from prepubertal lamb oocytes†.Biol Reprod. 2025 May 13;112(5):824-839. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioaf045. Biol Reprod. 2025. PMID: 40057970
-
HDAC1 and HDAC2 in mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos: Specificity versus compensation.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Jul;23(7):1119-27. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.31. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 27082454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic modifications during embryonic development: Gene reprogramming and regulatory networks.J Reprod Immunol. 2024 Sep;165:104311. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2024.104311. Epub 2024 Jul 20. J Reprod Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39047672 Review.
Cited by
-
The Mammalian Oocyte: A Central Hub for Cellular Reprogramming and Stemness.Stem Cells Cloning. 2025 Feb 18;18:15-34. doi: 10.2147/SCCAA.S513982. eCollection 2025. Stem Cells Cloning. 2025. PMID: 39991743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of the ubiquitin-specific protease (USP) gene family in cattle: primary analysis of muscle-specific USP genes and their influence on myogenesis.BMC Genomics. 2025 Aug 19;26(1):760. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11670-2. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40830755 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning and bioinformatics analysis of diagnostic biomarkers associated with the occurrence and development of lung adenocarcinoma.PeerJ. 2024 Jul 23;12:e17746. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17746. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39071134 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of ANXA3 and SOCS3 as biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction related to sphingolipid metabolism.Hereditas. 2025 Aug 4;162(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00515-3. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 40760666 Free PMC article.
-
Rise and SINE: roles of transcription factors and retrotransposons in zygotic genome activation.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025 Jan;26(1):68-79. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00772-6. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39358607
References
-
- Schultz R.M. The molecular foundations of the maternal to zygotic transition in the preimplantation embryo. Hum. Reprod. Update. 2002;8:323–331. - PubMed
-
- Burton A., Torres-Padilla M.E. Chromatin dynamics in the regulation of cell fate allocation during early embryogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014;15:723–734. - PubMed
-
- Tadros W., Lipshitz H.D. The maternal-to-zygotic transition: a play in two acts. Development. 2009;136:3033–3042. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

