Machine learning-based amide proton transfer imaging using partially synthetic training data
- PMID: 38098340
- PMCID: PMC10955622
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.29970
Machine learning-based amide proton transfer imaging using partially synthetic training data
Abstract
Purpose: Machine learning (ML) has been increasingly used to quantify CEST effect. ML models are typically trained using either measured data or fully simulated data. However, training with measured data often lacks sufficient training data, whereas training with fully simulated data may introduce bias because of limited simulations pools. This study introduces a new platform that combines simulated and measured components to generate partially synthetic CEST data, and to evaluate its feasibility for training ML models to predict amide proton transfer (APT) effect.
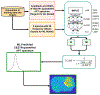
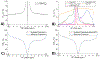
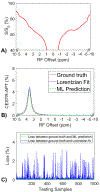
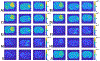
Methods: Partially synthetic CEST signals were created using an inverse summation of APT effects from simulations and the other components from measurements. Training data were generated by varying APT simulation parameters and applying scaling factors to adjust the measured components, achieving a balance between simulation flexibility and fidelity. First, tissue-mimicking CEST signals along with ground truth information were created using multiple-pool model simulations to validate this method. Second, an ML model was trained individually on partially synthetic data, in vivo data, and fully simulated data, to predict APT effect in rat brains bearing 9 L tumors.
Results: Experiments on tissue-mimicking data suggest that the ML method using the partially synthetic data is accurate in predicting APT. In vivo experiments suggest that our method provides more accurate and robust prediction than the training using in vivo data and fully synthetic data.
Conclusion: Partially synthetic CEST data can address the challenges in conventional ML methods.
Keywords: amide proton transfer; chemical exchange saturation transfer; machine learning; tumor.
© 2023 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures


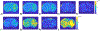
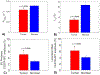
Update of
-
Amide Proton Transfer (APT) imaging in tumor with a machine learning approach using partially synthetic data.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 13:arXiv:2311.01683v2. ArXiv. 2023. Update in: Magn Reson Med. 2024 May;91(5):1908-1922. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29970. PMID: 37961738 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Amide Proton Transfer (APT) imaging in tumor with a machine learning approach using partially synthetic data.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 13:arXiv:2311.01683v2. ArXiv. 2023. Update in: Magn Reson Med. 2024 May;91(5):1908-1922. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29970. PMID: 37961738 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Enhancing amide proton transfer imaging in ischemic stroke using a machine learning approach with partially synthetic data.NMR Biomed. 2025 Jan;38(1):e5277. doi: 10.1002/nbm.5277. Epub 2024 Oct 21. NMR Biomed. 2025. PMID: 39434444 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging amide proton transfer and nuclear overhauser enhancement using chemical exchange rotation transfer (CERT).Magn Reson Med. 2014 Aug;72(2):471-6. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24953. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Magn Reson Med. 2014. PMID: 24302497 Free PMC article.
-
Amide proton transfer imaging of tumors: theory, clinical applications, pitfalls, and future directions.Jpn J Radiol. 2019 Feb;37(2):109-116. doi: 10.1007/s11604-018-0787-3. Epub 2018 Oct 19. Jpn J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30341472 Review.
-
Amide Proton Transfer-Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Imaging of Intracranial Brain Tumors and Tumor-like Lesions: Our Experience and a Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Feb 28;13(5):914. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13050914. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900058 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improving quantification accuracy of a nuclear Overhauser enhancement signal at -1.6 ppm at 4.7 T using a machine learning approach.Phys Med Biol. 2025 Jan 17;70(2):025009. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ada716. Phys Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39774035 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetry analysis of nuclear Overhauser enhancement effect at -1.6 ppm in ischemic stroke.Med Phys. 2025 May;52(5):2922-2937. doi: 10.1002/mp.17677. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 39933960 Free PMC article.
-
CEST MRI data analysis using Kolmogorov-Arnold network (KAN) and Lorentzian-KAN (LKAN) models.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Sep;94(3):1301-1317. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30548. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 40468586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou JY, van Zijl PCM. Chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging and spectroscopy. Prog Nucl Mag Res Sp 2006;48(2-3):109–136.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

