Craniofacial Distraction Osteogenesis
- PMID: 38098686
- PMCID: PMC10718658
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-1776298
Craniofacial Distraction Osteogenesis
Abstract
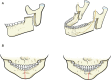
Distraction osteogenesis (DO) of the craniofacial skeleton has become an effective technique for the treatment of both nonsyndromic and syndromic conditions. The advent of craniofacial DO has allowed for earlier intervention in pediatric patients with less complication risk and morbidity compared to traditional techniques. In this review, we will discuss current application and technique for craniofacial DO by anatomical region and explore future applications in craniofacial surgery.
Keywords: craniofacial distraction; distraction osteogenesis; pediatric plastic surgery.
Thieme. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures
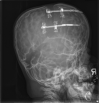

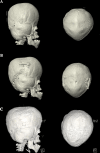

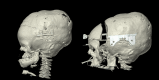

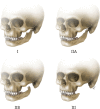

References
-
- Cherkashin A. Distraction osteogenesis: origins and evolution. Distraction Osteogenesis Tissue Eng. 1998;34:1–35.
-
- Al-Namnam N MN, Hariri F, Rahman Z AA. Distraction osteogenesis in the surgical management of syndromic craniosynostosis: a comprehensive review of published papers. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;56(05):353–366. - PubMed
-
- Garrigues G E, Ledford C, Fitch R D. Ilizarov: the man, the myth, the method. An orthopaedic inspiration. Duke Orthop J. 2013;3(01):104–107.
-
- Hopper R A, Ettinger R E, Purnell C A, Dover M S, Pereira A R, Tunçbilek G. Thirty years later: what has craniofacial distraction osteogenesis surgery replaced? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;145(06):1073e–1088e. - PubMed
-
- Mundinger G S, Rehim S A, Johnson O, III et al.Distraction osteogenesis for surgical treatment of craniosynostosis: a systematic review. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;138(03):657–669. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

