Serial attentional resource allocation during parallel feature value tracking
- PMID: 38099581
- PMCID: PMC10791127
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.91183
Serial attentional resource allocation during parallel feature value tracking
Abstract
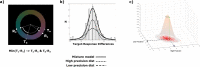
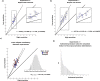
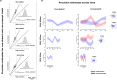
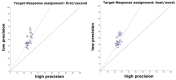
The visual system has evolved the ability to track features like color and orientation in parallel. This property aligns with the specialization of processing these feature dimensions in the visual cortex. But what if we ask to track changing feature-values within the same feature dimension? Parallel tracking would then have to share the same cortical representation, which would set strong limitations on tracking performance. We address this question by measuring the precision of color representations when human observers track the color of two superimposed dot clouds that simultaneously change color along independent trajectories in color-space. We find that tracking precision is highly imbalanced between streams and that tracking precision changes over time by alternating between streams at a rate of ~1 Hz. These observations suggest that, while parallel color tracking is possible, it is highly limited, essentially allowing for only one color-stream to be tracked with precision at a given time.
Keywords: attentional tracking; color vision; feature-based attention; human; neuroscience.
© 2023, Merkel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CM, LB, MB, MS, JH No competing interests declared
Figures

Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2023.09.12.557201
References
-
- Bartsch MV, Loewe K, Merkel C, Heinze HJ, Schoenfeld MA, Tsotsos JK, Hopf JM. Attention to color sharpens neural population tuning via feedback processing in the human visual cortex hierarchy. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2017;37:10346–10357. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0666-17.2017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

