Serum Ghrelin and Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Levels in Children with Prader-Willi and Bardet-Biedl Syndromes
- PMID: 38099591
- PMCID: PMC11590730
- DOI: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2023.2023-7-7
Serum Ghrelin and Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Levels in Children with Prader-Willi and Bardet-Biedl Syndromes
Abstract
Objective: Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) and Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) are causes of pediatric syndromic obesity. We aimed to investigate a possible role for ghrelin and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in the pathophysiology of PWS and BBS.
Methods: The study included 12 children with PWS, 12 children with BBS, 13 pediatric obese controls (OC) and 12 pediatric lean controls (LC). Fasting serum ghrelin and GLP-1 levels were measured by ELISA.
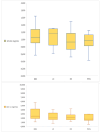
Results: In the PWS group, no significant difference was detected for median ghrelin levels when compared with OC and LC, which were 0.96 (0.69-1.15), 0.92 (0.72-1.20) and 1.13 (0.84-1.29) ng/mL, respectively. Similarly, there was no difference in PWS median GLP-1 levels when compared with OC and LC; 1.86 (1.5-2.94), 2.24 (1.62-2.78) and 2.06 (1.8-3.41) ng/mL, respectively. In the BBS group, there was no difference in median ghrelin levels when compared with OC and LC; 1.05 (0.87-1.51), 0.92 (0.72-1.20) and 1.13 (0.84-1.29) ng/mL, respectively. Neither was there a significant difference in median GLP-1 levels; 2.46 (1.91-4.17), 2.24 (1.62-2.78) and 2.06 (1.8-3.41) ng/mL for BBS, OC and LC, respectively.
Conclusion: There were no differences in median fasting ghrelin or GLP-1 levels when comparing patients with PWS and BBS with obese or lean peers. However, similar studies with larger series are needed.
Keywords: BBS; GLP-1; PWS; ghrelin.
©Copyright 2024 by Turkish Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes / The Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology published by Galenos Publishing House.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Muscogiuri G, Barrea L, Faggiano F, Maiorino MI, Parrillo M, Pugliese G, Ruggeri RM, Scarano E, Savastano S, Colao A, RESTARE Obesity in Prader-Willi syndrome: physiopathological mechanisms, nutritional and pharmacological approaches. J Endocrinol Invest . 2021;44(10):2057–2070. doi: 10.1007/s40618-021-01574-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Best S, Lord J, Roche M, Watson CM, Poulter JA, Bevers RPJ, Stuckey A, Szymanska K, Ellingford JM, Carmichael J, Brittain H, Toomes C, Inglehearn C, Johnson CA, Wheway G, Genomics England Research Consortium. Molecular diagnoses in the congenital malformations caused by ciliopathies cohort of the 100,000 Genomes Project. J Med Genet . 2021;59(8):1791–747. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2021-108065. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
