Wastewater surveillance for bacterial targets: current challenges and future goals
- PMID: 38099657
- PMCID: PMC10807411
- DOI: 10.1128/aem.01428-23
Wastewater surveillance for bacterial targets: current challenges and future goals
Abstract
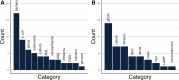
Wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) expanded rapidly in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. As the public health emergency has ended, researchers and practitioners are looking to shift the focus of existing wastewater surveillance programs to other targets, including bacteria. Bacterial targets may pose some unique challenges for WBE applications. To explore the current state of the field, the National Science Foundation-funded Research Coordination Network (RCN) on Wastewater Based Epidemiology for SARS-CoV-2 and Emerging Public Health Threats held a workshop in April 2023 to discuss the challenges and needs for wastewater bacterial surveillance. The targets and methods used in existing programs were diverse, with twelve different targets and nine different methods listed. Discussions during the workshop highlighted the challenges in adapting existing programs and identified research gaps in four key areas: choosing new targets, relating bacterial wastewater data to human disease incidence and prevalence, developing methods, and normalizing results. To help with these challenges and research gaps, the authors identified steps the larger community can take to improve bacteria wastewater surveillance. This includes developing data reporting standards and method optimization and validation for bacterial programs. Additionally, more work is needed to understand shedding patterns for potential bacterial targets to better relate wastewater data to human infections. Wastewater surveillance for bacteria can help provide insight into the underlying prevalence in communities, but much work is needed to establish these methods.IMPORTANCEWastewater surveillance was a useful tool to elucidate the burden and spread of SARS-CoV-2 during the pandemic. Public health officials and researchers are interested in expanding these surveillance programs to include bacterial targets, but many questions remain. The NSF-funded Research Coordination Network for Wastewater Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 and Emerging Public Health Threats held a workshop to identify barriers and research gaps to implementing bacterial wastewater surveillance programs.
Keywords: bacteria; wastewater surveillance; wastewater-based epidemiology.
Conflict of interest statement
RUH is managing member of AquaVitas, LLC and founder of the ASU non-profit project OneWaterOneHealth operating in the same intellectual space. LPS is employed by Ceres Nanosciences.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed W, Angel N, Edson J, Bibby K, Bivins A, O’Brien JW, Choi PM, Kitajima M, Simpson SL, Li J, Tscharke B, Verhagen R, Smith WJM, Zaugg J, Dierens L, Hugenholtz P, Thomas KV, Mueller JF. 2020. First confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: a proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community. Sci Total Environ 728:138764. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138764 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Naughton CC, Roman FA, Alvarado AGF, Tariqi AQ, Deeming MA, Bibby K, Bivins A, Rose JB, Medema G, Ahmed W, Katsivelis P, Allan V, Sinclair R, Zhang Y, Kinyua MN. 2021. Show us the data: global COVID-19 wastewater monitoring efforts, equity, and gaps. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2021.03.14.21253564 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

