MYOD-SKP2 axis boosts tumorigenesis in fusion negative rhabdomyosarcoma by preventing differentiation through p57Kip2 targeting
- PMID: 38102140
- PMCID: PMC10724275
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44130-0
MYOD-SKP2 axis boosts tumorigenesis in fusion negative rhabdomyosarcoma by preventing differentiation through p57Kip2 targeting
Abstract
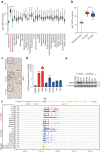
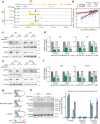
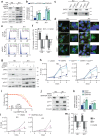
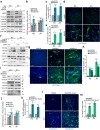
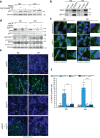
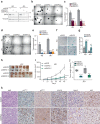
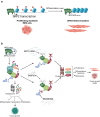
Rhabdomyosarcomas (RMS) are pediatric mesenchymal-derived malignancies encompassing PAX3/7-FOXO1 Fusion Positive (FP)-RMS, and Fusion Negative (FN)-RMS with frequent RAS pathway mutations. RMS express the master myogenic transcription factor MYOD that, whilst essential for survival, cannot support differentiation. Here we discover SKP2, an oncogenic E3-ubiquitin ligase, as a critical pro-tumorigenic driver in FN-RMS. We show that SKP2 is overexpressed in RMS through the binding of MYOD to an intronic enhancer. SKP2 in FN-RMS promotes cell cycle progression and prevents differentiation by directly targeting p27Kip1 and p57Kip2, respectively. SKP2 depletion unlocks a partly MYOD-dependent myogenic transcriptional program and strongly affects stemness and tumorigenic features and prevents in vivo tumor growth. These effects are mirrored by the investigational NEDDylation inhibitor MLN4924. Results demonstrate a crucial crosstalk between transcriptional and post-translational mechanisms through the MYOD-SKP2 axis that contributes to tumorigenesis in FN-RMS. Finally, NEDDylation inhibition is identified as a potential therapeutic vulnerability in FN-RMS.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Shern JF, et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis of rhabdomyosarcoma reveals a landscape of alterations affecting a common genetic axis in fusion-positive and fusion-negative tumors. Cancer Discov. 2014;4:216–31. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0639. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gryder BE, et al. PAX3–FOXO1 establishes myogenic super enhancers and confers BET Bromodomain Vulnerability. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:884–899. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-1297. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- 5x mille 9962/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Italian Association for Cancer Research)
- Ricerca Finalizzata GR-2013-02359212/Ministero della Salute (Ministry of Health, Italy)
- IG 27794/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Italian Association for Cancer Research)
- MFGA 22889/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Italian Association for Cancer Research)
- IG 10338/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Italian Association for Cancer Research)
- Ricerca Finalizzata GR-2016-02364546/Ministero della Salute (Ministry of Health, Italy)
- P30 CA045508/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- IG 15312/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Italian Association for Cancer Research)
- 5x mille/Ministero della Salute (Ministry of Health, Italy)
- IG 24696/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Italian Association for Cancer Research)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

