Chromosome-level genome assembly of the Stoliczka's Asian trident bat (Aselliscus stoliczkanus)
- PMID: 38102156
- PMCID: PMC10724287
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-023-02838-0
Chromosome-level genome assembly of the Stoliczka's Asian trident bat (Aselliscus stoliczkanus)
Abstract
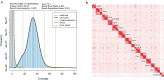
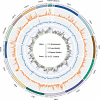
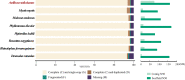
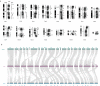
Stoliczka's Asian trident bat (Aselliscus stoliczkanus) is a small-bodied species and very sensitive to climate change. Here, we presented a chromosome-level genome assembly of A. stoliczkanus by combining Illumina sequencing, Nanopore sequencing and high-throughput chromatin conformation capture (Hi-C) sequencing technology. The genome assembly was 2.18 Gb in size with 98.26% of the genome sequences anchored onto 14 autosomes and two sex chromosomes (X and Y). The quality of the genome assembly is very high with a contig and scaffold N50 of 72.98 and 162 Mb, respectively, Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs (BUSCO) score of 96.6%, and the consensus quality value (QV) of 47.44. A total of 20,567 genes were predicted and 98.8% of these genes were functionally annotated. Syntenic blocks between A. stoliczkanus and Homo sapiens, together with previous comparative cytogenetic studies, provide valuable foundations for further comparative genomic and cytogenetic studies in mammals. The reference-quality genome of A. stoliczkanus contributes an important resource for conservative genomics and landscape genomics in predicting adaptation and vulnerability to climate change.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Đakrông virus, a novel mobatvirus (Hantaviridae) harbored by the Stoliczka's Asian trident bat (Aselliscus stoliczkanus) in Vietnam.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 15;9(1):10239. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46697-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31308502 Free PMC article.
-
The chromosome-level genome assembly of the giant dobsonfly Acanthacorydalis orientalis (McLachlan, 1899).Sci Data. 2024 Apr 8;11(1):351. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03194-3. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38589366 Free PMC article.
-
De novo assembly of a chromosome-level reference genome of red-spotted grouper (Epinephelus akaara) using nanopore sequencing and Hi-C.Mol Ecol Resour. 2019 Nov;19(6):1461-1469. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13064. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Mol Ecol Resour. 2019. PMID: 31325912 Free PMC article.
-
Author Correction: Đakrông virus, a novel mobatvirus (Hantaviridae) harbored by the Stoliczka's Asian trident bat (Aselliscus stoliczkanus) in Vietnam.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 15;10(1):760. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-57832-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31937908 Free PMC article.
-
A high-quality chromosomal-level genome assembly of Greater Scaup (Aythya marila).Sci Data. 2023 May 4;10(1):254. doi: 10.1038/s41597-023-02142-x. Sci Data. 2023. PMID: 37142629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dobson GE. On a new genus and species of Rhinolophidae, with description of a new species of Vesperus, and notes on some other species of insectivorous bats from Persia. J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal. 1871;40:455–461.
-
- Bates, P., Bumrungsri, S., Francis, C., Csorba, G. & Furey, N. Aselliscus stoliczkanus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008, e.T2155A9300617 (2008).
-
- Francis CM. A field guide to the mammals of South-East Asia. Mammalia. 2009;73:78–80.
-
- Zhang Z, et al. Variation in Aselliscus stoliczkanus based on morphology and molecular sequence data, with a new record of the genus Aselliscus in China. J. Mammal. 2016;97:1718–1727. doi: 10.1093/jmammal/gyw138. - DOI
-
- Tu, V., Görföl, T., Furey, N. & Csorba, G. Aselliscus stoliczkanus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2022, e.T214518902A21976509 (2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

