A review of foot-and-mouth disease in Ethiopia: epidemiological aspects, economic implications, and control strategies
- PMID: 38102688
- PMCID: PMC10724896
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-023-02263-0
A review of foot-and-mouth disease in Ethiopia: epidemiological aspects, economic implications, and control strategies
Abstract
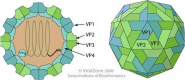
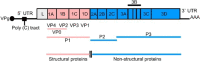
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is a contagious viral disease that affects the livelihoods and productivity of livestock farmers in endemic regions. It can infect various domestic and wild animals with cloven hooves and is caused by a virus belonging to the genus Aphthovirus and family Picornaviridae, which has seven different serotypes: A, O, C, SAT1, SAT2, SAT3, and Asia-1. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the molecular epidemiology, economic impact, diagnosis, and control measures of FMD in Ethiopia in comparison with the global situation. The genetic and antigenic diversity of FMD viruses requires a thorough understanding for developing and applying effective control strategies in endemic areas. FMD has direct and indirect economic consequences on animal production. In Ethiopia, FMD outbreaks have led to millions of USD losses due to the restriction or rejection of livestock products in the international market. Therefore, in endemic areas, disease control depends on vaccinations to prevent animals from developing clinical disease. However, in Ethiopia, due to the presence of diverse antigenic serotypes of FMD viruses, regular and extensive molecular investigation of new field isolates is necessary to perform vaccine-matching studies to evaluate the protective potential of the vaccine strain in the country.
Keywords: Control; Diagnosis; Economic importance; Epidemiology; Ethiopia; FMD; FMDV; Virus.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial or personal conflicts that could bias the review in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sero-prevalence, risk factors and distribution of foot and mouth disease in Ethiopia.Acta Trop. 2017 May;169:125-132. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2017.02.017. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Acta Trop. 2017. PMID: 28209551 Review.
-
A review of foot-and-mouth disease status and control measures in Botswana.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2023 Jul 28;55(4):278. doi: 10.1007/s11250-023-03674-5. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2023. PMID: 37500989 Review.
-
Foot and mouth disease outbreak investigation and estimation of its economic impact in selected districts in northwest Ethiopia.Vet Med Sci. 2020 Feb;6(1):122-132. doi: 10.1002/vms3.208. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Vet Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31710180 Free PMC article.
-
Foot-and-mouth disease in Asia.Virus Res. 2025 Jan;351:199514. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2024.199514. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Virus Res. 2025. PMID: 39689813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted FMD Vaccines for Eastern Africa: The AgResults Foot and Mouth Disease Vaccine Challenge Project.Viruses. 2021 Sep 14;13(9):1830. doi: 10.3390/v13091830. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34578411 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Determinants of Foot and Mouth Virus in Eastern Algeria.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2025 Apr 11;57(3):167. doi: 10.1007/s11250-025-04413-8. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2025. PMID: 40214836
-
Assessing farmers' willingness to pay for FMD vaccines and factors influencing payment: a contingent valuation study in central Oromia, Ethiopia.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Jul 15;20(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04169-7. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39010130 Free PMC article.
-
A unified Foot and Mouth Disease dataset for Uganda: evaluating machine learning predictive performance degradation under varying distributions.Front Artif Intell. 2024 Jul 31;7:1446368. doi: 10.3389/frai.2024.1446368. eCollection 2024. Front Artif Intell. 2024. PMID: 39144542 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing random forest predictive performance for foot and mouth disease outbreaks in Uganda: a calibrated uncertainty prediction approach for varying distributions.Front Artif Intell. 2024 Nov 1;7:1455331. doi: 10.3389/frai.2024.1455331. eCollection 2024. Front Artif Intell. 2024. PMID: 39554990 Free PMC article.
-
Diseases of Economic Importance in Feedlot Cattle in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Review with a Focus on Existing and Potential Options for Control.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jan 4;15(1):97. doi: 10.3390/ani15010097. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39795040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- CSA Agricultural sample survey 2020/21 [2013]. Report on livestock and livestock characteristics. Statistical Bulletin 589. Vol. II. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.," Ethiopia, 2021, vol. II. [Online]. Available: http://www.statsethiopia.gov.et/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/2013.LIVESTOC...
-
- Dabasa G, Abunna F. Review on Epidemiology of Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) in Ethiopia. J Trop Dis. 2021;9:269.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

