Effects of a multilevel intervention of resistance training with or without beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate in medical ICU patients during entire hospitalisation: a four-arm multicentre randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 38102705
- PMCID: PMC10724983
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-023-04698-x
Effects of a multilevel intervention of resistance training with or without beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate in medical ICU patients during entire hospitalisation: a four-arm multicentre randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Intensive care unit-acquired weakness (ICU-AW) is a prevalent and severe issue among ICU patients. Resistance training and beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB) intervention have demonstrated the potential to enhance muscle function in patients with sarcopenia and in older adults. The purpose of this study was to determine whether resistance training and/or HMB administration would improve physical function, muscle strength, and quality of life in medical ICU patients.
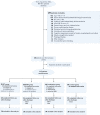
Methods: In this multicentre, four-arm, single-blind randomised control trial, a total of 112 adult patients with internal medical diagnoses admitted to the ICU were enrolled. These participants were then randomly assigned to one of four treatment groups: the resistance training group received protocol-based multilevel resistance exercise, the HMB group received 3 g/day of HMBCa, combination group and control groups received standard care, from the ICU to the general ward until discharge. The primary outcomes assessed at discharge included six-minute walking distance (6MWD) and short physical performance battery (SPPB). Secondary outcomes measured included muscle mass, MRC score, grip strength, and health reports quality of life at different time points. Data analysis was performed using a generalised linear mixed model, adhering to the principles of intention-to-treat analysis.
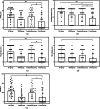
Results: Resistance training and combination treatment groups exhibited significant increases in SPPB scores (3.848 and 2.832 points, respectively) compared to the control group and substantial improvements in 6WMD (99.768 and 88.577 m, respectively) (all with P < 0.01). However, no significant changes were observed in the HMB group. Muscle strength, as indicated by MRC and grip strength tests conducted at both ICU and hospital discharge, showed statistically significant improvements in the resistance training and combination groups (P < 0.05). Nevertheless, no significant differences were found between the treatment groups and usual care in terms of 60-day mortality, prevalence of ICU-AW, muscle mass, quality of life, or other functional aspects.
Conclusions: Resistance training with or without beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate during the entire hospitalisation intervention improves physical function and muscle strength in medical ICU patients, but muscle mass, quality of life, and 60-day mortality were unaffected.
Trial registration: ChiCTR2200057685 was registered on March 15th, 2022.
Keywords: Beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate; Intensive care unit; Multicentre; Randomised controlled trial; Resistance training.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Supplementation with β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate after resistance training in post-acute care patients with sarcopenia: A randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2024 Apr;119:105323. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2023.105323. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38171034 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of resistance training and/or beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate supplementation on muscle mass, muscle strength and physical performance in older women with reduced muscle mass: protocol for a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2019 Feb 27;9(2):e025723. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025723. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 30819711 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methylbutyrate Supplementation on Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study.J Nutr Health Aging. 2023;27(5):329-339. doi: 10.1007/s12603-023-1911-1. J Nutr Health Aging. 2023. PMID: 37248756 Clinical Trial.
-
Elderly persons with ICU-acquired weakness: the potential role for β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB) supplementation?JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2014 Jul;38(5):567-75. doi: 10.1177/0148607113502545. Epub 2013 Sep 26. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24072740 Review.
-
β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate and its impact on skeletal muscle mass and physical function in clinical practice: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Am J Clin Nutr. 2019 Apr 1;109(4):1119-1132. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy373. Am J Clin Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30982854
Cited by
-
Multidisciplinary collaborative approach to cardiopulmonary rehabilitation in cancer patients with intensive care unit-acquired weakness: a clinical efficacy and safety analysis.Am J Cancer Res. 2025 May 25;15(5):2427-2438. doi: 10.62347/UVQC5990. eCollection 2025. Am J Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40520875 Free PMC article.
-
Association between whole blood ratio and risk of mortality in massively transfused trauma patients: retrospective cohort study.Crit Care. 2024 Jul 19;28(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s13054-024-05041-8. Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 39030579 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcopenia and frailty in critical illness.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2025 May 1;28(3):192-199. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000001123. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2025. PMID: 40072495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Sarcopenia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Its Incidence and Muscle Parameter Shifts During Hospitalisation.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025 Feb;16(1):e13662. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13662. Epub 2024 Dec 17. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025. PMID: 39690131 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-hydroxy-beta-methyl butyrate supplementation in critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 23;12:1505797. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1505797. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39917745 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NO: 2021Y0051/Guidance project of Fujian Provincial Science and Technology Department, China
- NO: 2021Y0051/Guidance project of Fujian Provincial Science and Technology Department, China
- NO: 2021Y0051/Guidance project of Fujian Provincial Science and Technology Department, China
- NO: 2021Y0051/Guidance project of Fujian Provincial Science and Technology Department, China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

