Distinctive physical properties of DNA shared by RNA polymerase II gene promoters and 5'-flanking regions of tRNA genes
- PMID: 38102732
- PMCID: PMC11005993
- DOI: 10.1093/jb/mvad111
Distinctive physical properties of DNA shared by RNA polymerase II gene promoters and 5'-flanking regions of tRNA genes
Abstract
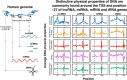
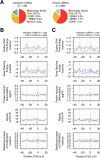
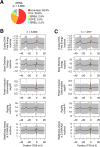
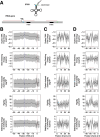
Numerous noncoding (nc)RNAs have been identified. Similar to the transcription of protein-coding (mRNA) genes, long noncoding (lnc)RNA genes and most of micro (mi)RNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II (Pol II). In the transcription of mRNA genes, core promoters play an indispensable role; they support the assembly of the preinitiation complex (PIC). However, the structural and/or physical properties of the core promoters of lncRNA and miRNA genes remain largely unexplored, in contrast with those of mRNA genes. Using the core promoters of human genes, we analyzed the repertoire and population ratios of residing core promoter elements (CPEs) and calculated the following five DNA physical properties (DPPs): duplex DNA free energy, base stacking energy, protein-induced deformability, rigidity and stabilizing energy of Z-DNA. Here, we show that their CPE and DPP profiles are similar to those of mRNA gene promoters. Importantly, the core promoters of these three classes of genes have two highly distinctive sites in their DPP profiles around the TSS and position -27. Similar characteristics in DPPs are also found in the 5'-flanking regions of tRNA genes, indicating their common essential roles in transcription initiation over the kingdom of RNA polymerases.
Keywords: Core promoter; lncRNA; miRNA; physical properties of DNA; protein-coding gene; tRNA.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Japanese Biochemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Core Promoter Regions of Antisense and Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 3;24(9):8199. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098199. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175907 Free PMC article.
-
Widespread use of TATA elements in the core promoters for RNA polymerases III, II, and I in fission yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Oct;21(20):6870-81. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.20.6870-6881.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11564871 Free PMC article.
-
Ssl2/TFIIH function in transcription start site scanning by RNA polymerase II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Elife. 2021 Oct 15;10:e71013. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71013. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34652274 Free PMC article.
-
How to Recruit the Correct RNA Polymerase? Lessons from snRNA Genes.Trends Genet. 2019 Jun;35(6):457-469. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2019.04.001. Epub 2019 Apr 27. Trends Genet. 2019. PMID: 31040056 Review.
-
Interplay between the transcription preinitiation complex and the +1 nucleosome.Trends Biochem Sci. 2024 Feb;49(2):145-155. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2023.12.001. Epub 2024 Jan 13. Trends Biochem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38218671 Review.
Cited by
-
Physical Peculiarity of Two Sites in Human Promoters: Universality and Diverse Usage in Gene Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 25;25(3):1487. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031487. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338773 Free PMC article.
-
The miRNomics of antiretroviral therapy-induced obesity.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Apr 5;25(1):81. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01585-2. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40186666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keep calm and reboot - how cells restart transcription after DNA damage and DNA repair.FEBS Lett. 2025 Jan;599(2):275-294. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14964. Epub 2024 Jul 11. FEBS Lett. 2025. PMID: 38991979 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Friedländer, M.R., Chen, W., Adamidi, C., Maaskola, J., Einspanier, R., Knespel, S., and Rajewsky, N. (2008) Discovering microRNAs from deep sequencing data using miRDeep. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 407–415 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

