Human Hepatocyte Transplantation: Three Decades of Clinical Experience and Future Perspective
- PMID: 38103170
- PMCID: PMC10940836
- DOI: 10.1093/stcltm/szad084
Human Hepatocyte Transplantation: Three Decades of Clinical Experience and Future Perspective
Abstract
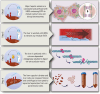
Orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) is the current standard of care for both chronic and acute terminal liver disease. However, a major limitation of this treatment is the shortage of healthy donor organs and the need for life-long immunosuppression to prevent graft rejection. Hepatocyte transplantation (HTx) has emerged as a promising, alternative therapeutic approach to either replace OLT or to act as a bridge until a donor liver becomes available thus reducing waiting list mortality. HTx involves the infusion and engraftment of human hepatocytes, typically isolated from organs unsuitable for OLT, into recipient liver parenchyma to carry out the missing hepatic function of the native cells. HTx is less invasive than OLT and can be performed repeatedly if required. The safety of clinical HTx has been shown and treatment results are promising, especially in patients with liver-based metabolic disorders. Nevertheless, HTx has failed to become the standard of care treatment for such disorders. This review aims to evaluate the progress that has been made within the field of HTx over the last 30 years and identify potential shortcomings within the approach which may be hindering its routine clinical application.
Keywords: acute liver failure; cell therapy; hepatocyte transplantation; liver-based metabolic disorders.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
A.D. declared member of advisory board of Ambys, Aspect Biosystems, Promethera; honoraria from Alexion, Univar. The other authors declared no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mito M, Kusano M, Kawaura Y.. Hepatocyte transplantation in man. Transplant Proc. 1992;24(6):3052-3053. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical