Cognitive trajectories in longitudinally trained 3xTg-AD mice
- PMID: 38103626
- PMCID: PMC10872326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2023.114435
Cognitive trajectories in longitudinally trained 3xTg-AD mice
Abstract
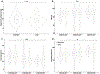
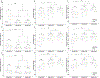
Preclinical studies in Alzheimer's disease (AD) often rely on cognitively naïve animal models in cross-sectional designs that can fail to reflect the cognitive exposures across the lifespan and heterogeneous neurobehavioral features observed in humans. To determine whether longitudinal cognitive training may affect cognitive capacities in a well-characterized AD mouse model, 3xTg and wild-type mice (n = 20) were exposed daily to a training variant of the Go-No-Go (GNG) operant task from 3 to 9 months old. At 3, 6, and 9 months, performance on a testing variant of the GNG task and anxiety-like behaviors were measured, while long-term recognition memory was also assessed at 9 months. In general, GNG training improved performance with increasing age across genotypes. At 3 months old, 3xTg mice showed slight deficits in inhibitory control that were accompanied by minor improvements in signal detection and decreased anxiety-like behavior, but these differences did not persist at 6 and 9 months old. At 9 months old, 3xTg mice displayed minor deficits in signal detection, and long-term recognition memory capacity was comparable with wild-type subjects. Our findings indicate that longitudinal cognitive training can render 3xTg mice with cognitive capacities that are on par with their wild-type counterparts, potentially reflecting functional compensation in subjects harboring AD genetic mutations.
Keywords: 3xTg; Alzheimer's disease; Cognitive training; Go-No-Go; Resilience.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing of Interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

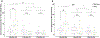
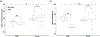
Similar articles
-
Short-term modern life-like stress exacerbates Aβ-pathology and synapse loss in 3xTg-AD mice.J Neurochem. 2015 Sep;134(5):915-26. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13195. Epub 2015 Jul 14. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26077803 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine stress responsivity and social memory in 3xTg-AD female and male mice: A tale of two experiments.Horm Behav. 2020 Nov;126:104852. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2020.104852. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Horm Behav. 2020. PMID: 32949555
-
Restoration of dopamine release deficits during object recognition memory acquisition attenuates cognitive impairment in a triple transgenic mice model of Alzheimer's disease.Learn Mem. 2012 Sep 14;19(10):453-60. doi: 10.1101/lm.026070.112. Learn Mem. 2012. PMID: 22984283
-
Early detection of cognitive deficits in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Behav Brain Res. 2015 Aug 1;289:29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.04.012. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25896362
-
Alcohol drinking exacerbates neural and behavioral pathology in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019;148:169-230. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2019.10.017. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31733664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
rTMS Modulation of Behavioral and Biological Measures in 3xTg-AD Mice.Brain Sci. 2024 Nov 26;14(12):1186. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14121186. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39766385 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental laboratory models as tools for understanding modifiable dementia risk.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Jun;20(6):4260-4289. doi: 10.1002/alz.13834. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 38687209 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oddo S et al., “Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease with plaques and tangles: intracellular Aβ and synaptic dysfunction,” Neuron, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 409–421, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Oddo S, Caccamo A, Kitazawa M, Tseng BP, and LaFerla FM, “Amyloid deposition precedes tangle formation in a triple transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease,” Neurobiology of aging, vol. 24, no. 8, pp. 1063–1070, 2003. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

